The long-term efficacy of STN vs GPi deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30170458
- PMCID: PMC6393030
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012153
The long-term efficacy of STN vs GPi deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis assessed the long-term efficacy of deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) and globus pallidus interna (GPi) for Parkinson disease (PD).
Methods: PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials databases were searched. Outcomes were unified Parkinson disease rating scale section (UPDRS) III off-medication score, Parkinson's disease questionnaire: 39 activities of daily living (PDQ-39 ADL) score, and levodopa-equivalent dosage after DBS.
Results: During the off-medication state, pooled weighted mean difference (WMD) of UPDRS III score was .69 (95% confidence interval [CI] = -1.77 to 3.16, P = .58). In subgroup analysis, WMD of UPDRS III off-medication scores from baseline to 2 years and 3 years post-DBS were -.61 (95% CI = -2.97 to 1.75, P = .61) and 2.59 (95% CI = -2.30 to 7.47, P = .30). Pooled WMD of changes in tremor, rigidity, and gait scores were 1.12 (95% CI = -0.05 to 2.28, P = .06), 1.22 (95% CI = -0.51 to 2.94, P = .17) and .37 (95% CI = -0.13 to 0.87, P = .15), respectively. After DBS, pooled WMD of PDQ-39 ADL and LED were -3.36 (95% CI = -6.36 to -0.36, P = .03) and 194.89 (95% CI = 113.16 to 276.63, P < .001).
Conclusions: STN-DBS and GPi-DBS improve motor function and activities of daily living for PD. Differences in the long-term efficacy for PD on motor symptoms were not observed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
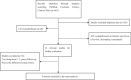





References
-
- Yao SC, Hart AD, Terzella MJ. An evidence-based osteopathic approach to Parkinson disease. Osteopath Fam Physician 2013;5:96–101.
-
- Bonuccelli U. Comparing dopamine agonists in Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurol 2003;16(suppl 1):S13–9. - PubMed
-
- Pahwa R, Factor SA, Lyons KE, et al. Practice parameter: treatment of Parkinson disease with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia (an evidence based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2006;66:983–95. - PubMed
-
- The Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's Disease Study Group. Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 2001;345:956–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

