Initiating base excision repair in chromatin
- PMID: 30170831
- PMCID: PMC6340775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.08.011
Initiating base excision repair in chromatin
Abstract
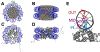
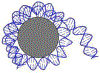
The base excision repair (BER) pathway removes modified nucleobases that can be deleterious to an organism. BER is initiated by a glycosylase, which finds and removes these modified nucleobases. Most of the characterization of glycosylase activity has been conducted in the context of DNA oligomer substrates. However, DNA within eukaryotic organisms exists in a packaged environment with the basic unit of organization being the nucleosome core particle (NCP). The NCP is a complex substrate for repair in which a variety of factors can influence glycosylase activity. In this Review, we focus on the geometric positioning of modified nucleobases in an NCP and the consequences on glycosylase activity and initiating BER.
Keywords: Base excision repair; Chromatin; DNA damage; DNA repair; Glycosylase; Nucleosome.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

