A comparison of different methods of red blood cell leukoreduction and additive solutions on the accumulation of neutrophil-priming activity during storage
- PMID: 30171813
- PMCID: PMC6131068
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.14788
A comparison of different methods of red blood cell leukoreduction and additive solutions on the accumulation of neutrophil-priming activity during storage
Abstract
Background: Three methods of leukoreduction (LR) are used worldwide: filtration, buffy coat removal (BCR), and a combination of the previous two methods. Additionally, there are a number of additive solutions (ASs) used to preserve red blood cell (RBC) function throughout storage. During RBC storage, proinflammatory activity accumulates; thus, we hypothesize that both the method of LR and the AS affect the accumulation of proinflammatory activity.
Study design and methods: Ten units of whole blood were drawn from healthy donors, the RBC units were isolated, divided in half by weight, and leukoreduced by: 1) BCR, 2) filtration, or 3) BCR and filtration (combination-LR); stored in bags containing AS-3 per AABB criteria; and sampled weekly. The supernatants were isolated and frozen (-80°C). RBC units drawn from healthy donors into AS-1-, AS-3-, or AS-5-containing bags were also stored and sampled weekly, and the supernatants were isolated and frozen. The supernatants were assayed for neutrophil (PMN)-priming activity and underwent proteomic analyses.
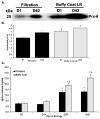
Results: Filtration and combination LR decreased priming activity accumulation versus buffy coat LR, although the accumulation of priming activity was not different during storage. Combination LR increased hemolysis versus filtration via proteomic analysis. Priming activity from AS-3 units was significant later in storage versus AS-1- or AS-5-stored units.
Conclusions: Although both filtration and combination LR decrease the accumulation of proinflammatory activity versus buffy coat LR, combination LR is not more advantageous over filtration, has increased costs, and may cause increased hemolysis. In addition, AS-3 decreases the early accumulation of PMN-priming activity during storage versus AS-1 or AS-5.
© 2018 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest with the submitted manuscript
Figures
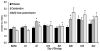
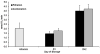
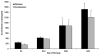
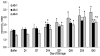
References
-
- Novotny VM, van DR, Witvliet MD, Claas FH, Brand A. Occurrence of allogeneic HLA and non-HLA antibodies after transfusion of prestorage filtered platelets and red blood cells: a prospective study. Blood. 1995 Apr 1;85(7):1736–41. - PubMed
-
- Khan SY, Kelher MR, Heal JM, Blumberg N, Boshkov LK, Phipps R, Gettings KF, McLaughlin NJ, Silliman CC. Soluble CD40 ligand accumulates in stored blood components, primes neutrophils through CD40, and is a potential cofactor in the development of transfusion-related acute lung injury. Blood. 2006 Oct 1;108(7):2455–62. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fisher M, Chapman JR, Ting A, Morris PJ. Alloimmunisation to HLA antigens following transfusion with leucocyte-poor and purified platelet suspensions. Vox Sang. 1985;49(5):331–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

