DNA hypermethylation-mediated downregulation of antioxidant genes contributes to the early onset of cataracts in highly myopic eyes
- PMID: 30172102
- PMCID: PMC6122317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.08.012
DNA hypermethylation-mediated downregulation of antioxidant genes contributes to the early onset of cataracts in highly myopic eyes
Abstract
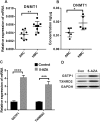
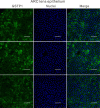
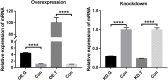
High myopia is recognized as a risk factor for earlier onset of nuclear cataracts. One possible explanation for this is that lenses in highly myopic eyes are exposed to higher levels of oxygen than normal eyes owing to earlier vitreous liquefaction and, hence, are subjected to oxidative insults. Here, we first compared the methylation levels of six essential antioxidant genes (GSTP1, NRF2, OGG1, TXN, TXNRD1 and TXNRD2) between highly myopic cataract (HMC) and age-related cataract (ARC) lens epithelial samples via Sequenom MassARRAY. We found that specific CpG units in the promoters of GSTP1 and TXNRD2 were hypermethylated and that the expression levels of these two genes were lower in the HMC group than in the ARC group. A luciferase reporter assay confirmed the significance of differentially methylated fragments in the activation of transcription. The importance of GSTP1 and TXNRD2 in antioxidant capacity was confirmed by overexpression or knockdown experiments on cultured lens epithelial cells (LECs). In addition, the expression of DNA methyl transferase 1 (DNMT1) was higher in the lens epithelium of HMC patients than that of ARC patients, and the expression of GSTP1 and TXNRD2 was upregulated by use of a DNMT inhibitor in cultured LECs. Finally, we mimicked the intraocular environment of highly myopic eyes by treating LECs with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and observed both alterations in the methylation status of the GSTP1 and TXNRD2 promoters and time-dependent altered expression levels. Therefore, we propose that in an environment with high oxygen, in which lenses in highly myopic eyes are immersed, there exists a vicious cycle composed of increased oxidative stress and decreased enzymatic antioxidants via the hypermethylation of antioxidant genes.
Keywords: Cataract; DNA methylation; GSTP1; High myopia; Oxidative stress; TXNRD2.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures















References
-
- Kubo E. Axial length, myopia, and the severity of lens opacity at the time of cataract surgery. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2006;124(11):1586–1590. - PubMed
-
- Pan C.W. Myopia, axial length, and age-related cataract: the Singapore Malay eye study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013;54(7):4498–4502. - PubMed
-
- Sun J. High prevalence of myopia and high myopia in 5060 Chinese university students in Shanghai. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012;53(12):7504–7509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

