Quantitative Activity Profile and Context Dependence of All Human 5' Splice Sites
- PMID: 30174293
- PMCID: PMC6179149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.033
Quantitative Activity Profile and Context Dependence of All Human 5' Splice Sites
Abstract
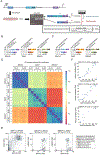
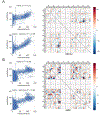
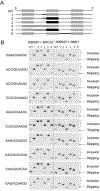
Pre-mRNA splicing is an essential step in the expression of most human genes. Mutations at the 5' splice site (5'ss) frequently cause defective splicing and disease due to interference with the initial recognition of the exon-intron boundary by U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), a component of the spliceosome. Here, we use a massively parallel splicing assay (MPSA) in human cells to quantify the activity of all 32,768 unique 5'ss sequences (NNN/GYNNNN) in three different gene contexts. Our results reveal that although splicing efficiency is mostly governed by the 5'ss sequence, there are substantial differences in this efficiency across gene contexts. Among other uses, these MPSA measurements facilitate the prediction of 5'ss sequence variants that are likely to cause aberrant splicing. This approach provides a framework to assess potential pathogenic variants in the human genome and streamline the development of splicing-corrective therapies.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
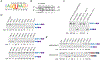

References
-
- Bertram K, Agafonov D, Dybkov O, Haselbach D, Leelaram MN, Will CL, Urlaub H, Kastner B, Luhrmann R, and Stark H (2017). Cryo-EM structure of a pre-catalytic human spliceosome primed for activation. Cell 170, 701–713. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Chives M, Romano M, Baralle M, Kralovicova J, Barallel F, Krainer A, and Vorechovsky I (2007). Aberrant 5’ splice sites in human disease genes: mutation pattern, nucleotide structure and comparison of computational tools that predict their utilization. Nucleic Acids Res 35, 4250–6. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

