Time-Restricted Feeding Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice Lacking a Circadian Clock
- PMID: 30174302
- PMCID: PMC7751278
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.004
Time-Restricted Feeding Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice Lacking a Circadian Clock
Abstract
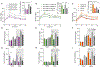
Increased susceptibility of circadian clock mutant mice to metabolic diseases has led to the idea that a molecular clock is necessary for metabolic homeostasis. However, these mice often lack a normal feeding-fasting cycle. We tested whether time-restricted feeding (TRF) could prevent obesity and metabolic syndrome in whole-body Cry1;Cry2 and in liver-specific Bmal1 and Rev-erbα/β knockout mice. When provided access to food ad libitum, these mice rapidly gained weight and showed genotype-specific metabolic defects. However, when fed the same diet under TRF (food access restricted to 10 hr during the dark phase) they were protected from excessive weight gain and metabolic diseases. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses showed that TRF reduced the accumulation of hepatic lipids and enhanced cellular defenses against metabolic stress. These results suggest that the circadian clock maintains metabolic homeostasis by sustaining daily rhythms in feeding and fasting and by maintaining balance between nutrient and cellular stress responses.
Keywords: cell response to stress; circadian clock; circadian clock mutant mice; feeding-fasting rhythms; hepatic metabolomics; hepatic transcriptomics; metabolic diseases; metabolic homeostasis; metabolic syndrome; time-restricted feeding.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests
SP is the author of a book titled “The Circadian Code” and he collects author’s royalty.
Figures
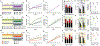





Comment in
-
Benefits of time-restricted feeding.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 Nov;14(11):626. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0093-2. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30218015 No abstract available.
References
-
- Asher G, and Sassone-Corsi P (2015). Time for food: the intimate interplay between nutrition, metabolism, and the circadian clock. Cell 161, 84–92. - PubMed
-
- Barclay JL, Shostak A, Leliavski A, Tsang AH, Johren O, Muller-Fielitz H, Landgraf D, Naujokat N, van der Horst GT, and Oster H (2013). High-fat diet-induced hyperinsulinemia and tissue-specific insulin resistance in Cry-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304, E1053–1063. - PubMed
-
- Bass J (2012). Circadian topology of metabolism. Nature 491, 348–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

