Comparison of incision size and intraocular lens performance after implantation with three preloaded systems and one manual delivery system
- PMID: 30174410
- PMCID: PMC6109656
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S166776
Comparison of incision size and intraocular lens performance after implantation with three preloaded systems and one manual delivery system
Abstract
Purpose: To compare corneal incision size and intraocular lens (IOL) performance/behavior following implantation with the following delivery systems: system U (UltraSert®), system S (Hoya iSert® 250/251), system T (Tecnis® iTec), and a manual system (Monarch® III Delivery System).
Setting: Six study sites (four in Spain and two in France).
Design: Prospective, multicenter, parallel-group, randomized, subject-masked, postmarket clinical study.
Materials and methods: Subjects were enrolled based on predetermined inclusion/exclusion criteria. The effectiveness end points compared corneal incision size and enlargement after IOL implantation (day of surgery) among all delivery systems. Exploratory end points included mean enlargement of corneal incision size, rates of trapped trailing haptic, IOL adherence to the plunger tip, nozzle tip splitting, and mean surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) at postoperative visit.
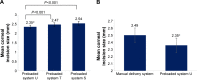
Results: One hundred and nine subjects participated in the study. The mean corneal incision size following IOL implantation was 2.35±0.019 mm for system U, 2.47±0.016 mm for system T, 2.54±0.019 mm for system S, and 2.49±0.011 mm for the manual system. There were five instances of trapped trailing haptic (all system T group, N=26), one instance of IOL adherence to the plunger tip (system S group, N=26), and six instances of nozzle tip splitting (all system S group, N=26). System U had the least SIA (postoperative Day 1) (SIA Centroid = 0.10 diopters [axis: 83.06°]).
Conclusion: Preloaded delivery system U supported the completion of surgery with the smallest incision size, the least SIA (postoperative Day 1), and no trapped trailing haptics or nozzle tip splitting compared to two other preloaded systems and one manual system.
Keywords: UltraSert; corneal incision; intraocular lens; preloaded IOL injector.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Lixin Wang, MD, PhD, is a full-time employee of Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Aldo A Martinez, PhD, is a full-time employee of Alcon Laboratories, Inc. Javier Mendicute, MD, PhD, is a consultant for Alcon Laboratories, Inc., and received research support from Alcon Laboratories, Inc., AcuFocus, Inc., MEDICEM, Novagali Pharma S.A., and Carl Zeiss Meditec, Inc. Thierry Amzallag, MD, has received personal fees from Alcon Laboratories, Cutting Edge, and Théa, and is a clinical trial investigator for Zeiss. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

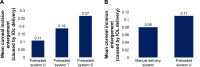
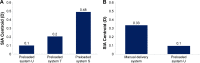
Similar articles
-
Experimental Study on Delivery Performance of an Automated Preloaded Intraocular Lens Injector System for Corneal and Sclerocorneal Incisions.J Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar 31;2021:5548493. doi: 10.1155/2021/5548493. eCollection 2021. J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33859834 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro delivery performance assessment of a new preloaded intraocular lens delivery system.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016 Dec;42(12):1814-1820. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2016.10.014. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016. PMID: 28007114
-
In vitro comparison of delivery performance of 4 preloaded intraocular lens injector systems for corneal and sclerocorneal incisions.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2019 Jun;45(6):840-846. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.10.050. Epub 2019 Mar 8. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 30853318
-
Characterisation of Intraocular Lens Injectors.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2024 Aug;241(8):905-916. doi: 10.1055/a-2349-2158. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2024. PMID: 39146575 Review. English.
-
[Sutureless scleral intraocular lens fixation: report of nine cases and literature review].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2013 Oct;36(8):658-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2012.09.009. Epub 2013 Jul 25. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2013. PMID: 23891322 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Experimental analysis of recommended corneal incision sizes in cataract surgery using 13 intraocular lens injector systems.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 15;13(1):2659. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29497-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36792674 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Study on Delivery Performance of an Automated Preloaded Intraocular Lens Injector System for Corneal and Sclerocorneal Incisions.J Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar 31;2021:5548493. doi: 10.1155/2021/5548493. eCollection 2021. J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33859834 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Evaluation of a Novel Preloaded Intraocular Lens Delivery System During Routine Cataract Surgery.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 Aug 12;14:2291-2300. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S260925. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32943830 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter Evaluation of Time, Operational, and Economic Efficiencies of a New Preloaded Intraocular Lens Delivery System versus Manual Intraocular Lens Delivery.Clin Ophthalmol. 2021 Feb 16;15:591-599. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S263658. eCollection 2021. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33623360 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Visual, Refractive, and Functional Outcomes after Implantation of an Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lens in Patients with Stable and Mild Glaucoma.Ophthalmol Ther. 2025 May;14(5):1039-1051. doi: 10.1007/s40123-025-01124-z. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Ophthalmol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40128495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Endophthalmitis Study Group, European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons Prophylaxis of postoperative endophthalmitis following cataract surgery: results of the ESCRS multicenter study and identification of risk factors. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33(6):978–988. - PubMed
-
- Alió JL, Schimchak P, Montés-Micó R, Galal A. Retinal image quality after microincision intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(8):1557–1560. - PubMed
-
- Kahraman G, Amon M, Franz C, Prinz A, Abela-Formanek C. Intraindividual comparison of surgical trauma after bimanual microincision and conventional small-incision coaxial phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33(4):618–622. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu K, Kobayashi K, Takayama S, Zhaobin G. Preloaded injector for intraocular lens implantation without the use of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34(7):1157–1160. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

