Analysis of the clinical significance of DCLK1+ colorectal cancer using novel monoclonal antibodies against DCLK1
- PMID: 30174443
- PMCID: PMC6110630
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S169928
Analysis of the clinical significance of DCLK1+ colorectal cancer using novel monoclonal antibodies against DCLK1
Abstract
Introduction: Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) is considered a putative tumor stem cell (TSC) marker and a promising therapeutic target, as DCLK1+ progeny cells exhibit high expression in tumors. However, the biological function of DCLK1+ cells in tumorigenesis and tumor progression remains unclear.
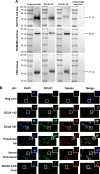
Materials and methods: We generated rabbit monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against DCLK1, DCLK1-42, and DCLK1-87 mAbs, using a novel chip-based immunospot array assay on a chip system. First, the specificity of two mAbs to DCLK1 was confirmed by Western blot, which were bound to DCLK1-long in normal colon cells and to DCLK1-short in a cancer cell line as well as colorectal cancer (CRC) cells.
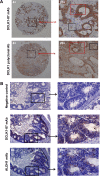
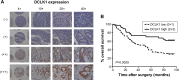
Results: Precise localization analysis using immunofluorescence revealed that both mAbs had cytoplasmic signal and exhibited a high degree of overlap with microtubules. Furthermore, bacterial display technology indicated that the antigenic epitope region of DCLK1-87 mAb was consistent with that of a commercial anti-DCLK1 polyclonal antibody. In addition, DCLK1-42 mAb has the common polyclonal antibody characteristic of binding to more than one site on DCLK1. By immunohistochemistry, it was found that DCLK1-87 mAb was more specific for DCLK1+ cell labeling than a commercial anti-DCLK1 polyclonal antibody. DCLK1 labeled with DCLK1-87 mAb might be a potential TSC marker because the tissue expression site covers the ALDH1 area in CRC tissues. Finally, we analyzed 100 pairs of cancer tissues and matching paracancerous tissue samples from patients with CRC who received 100 months of follow-up with the DCLK1-87 mAb. The results showed that patients with high DCLK1 expression exhibited a longer survival time than that of patients with low DCLK1 expression (P=0.0029).
Discussion: Our results indicated that we successfully generated an efficient tool for the precise detection of DCLK1+ cells in cancer tissues. Moreover, we found that high DCLK1 expression in CRC patients appears to play a protective role against tumor progression.
Keywords: DCLK1 monoclonal antibodies; colorectal cancer; doublecortin-like kinase 1; epitope; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Burgess HA, Martinez S, Reiner O. KIAA0369, doublecortin-like kinase, is expressed during brain development. J Neurosci Res. 1999;58(4):567–575. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi H, Tanaka T, Gleeson JG. Doublecortin-like kinase functions with doublecortin to mediate fiber tract decussation and neuronal migration. Neuron. 2006;49(1):55–66. - PubMed
-
- May R, Riehl TE, Hunt C, Sureban SM, Anant S, Courtney WH. Identification of a novel putative gastrointestinal stem cell and adenoma stem cell marker, doublecortin and CaM kinase-like-1, following radiation injury and in adenomatous polyposis coli/multiple intestinal neoplasia mice. Stem Cells. 2008;26(3):630–637. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

