miR-34a Regulates Multidrug Resistance via Positively Modulating OAZ2 Signaling in Colon Cancer Cells
- PMID: 30175154
- PMCID: PMC6098920
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7498514
miR-34a Regulates Multidrug Resistance via Positively Modulating OAZ2 Signaling in Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
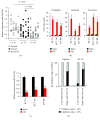
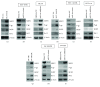
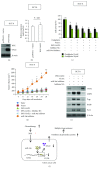
Although aberrant expression of miR-34a, an essential tumor suppressor miRNA, has been frequently observed in colon cancer (CCa), whether miR-34a can regulate CCa progression by modulating other facets of this malignancy (such as multidrug resistance, MDR) remains unknown. Here, we report for the first time that miR-34a expression was significantly downregulated in clinical CCa samples from oxaliplatin-resistant patients and in experimentally established multidrug-resistant CCa cells. By using histoculture drug response assay, we further confirmed that clinical CCa samples with lower miR-34a expression appeared to be more resistant to chemotherapy. Functionally, ectopic expression of exogenous miR-34a resensitized multidrug-resistant HCT-8/OR cells to oxaliplatin treatment, whereas miR-34a inhibition augmented the oxaliplatin resistance in chemosensitive HCT-8 cells. Mechanistically, miR-34a positively regulated the mRNA stability of the ornithine decarboxylase antizyme 2 (OAZ2) by directly targeting its three prime untranslated region (3'UTR). Consequently, suppression of the expression of miR-34a/OAZ2 signaling by chemotherapeutic agents significantly enhanced the activation of MDR-associated ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters and antiapoptosis pathways, thus leading to MDR development in CCa cells. Collectively, our combined analysis reveals a critical role of miR-34a/OAZ2 cascade in conferring a proper cellular response to CCa chemotherapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Overexpressing microRNA-34a overcomes ABCG2-mediated drug resistance to 5-FU in side population cells from colon cancer via suppressing DLL1.J Biochem. 2020 Jun 1;167(6):557-564. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaa012. J Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32044957
-
miR-409-3p sensitizes colon cancer cells to oxaliplatin by inhibiting Beclin-1-mediated autophagy.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Apr;37(4):1030-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2492. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26935807
-
MicroRNA-137 chemosensitizes colon cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic drug oxaliplatin (OXA) by targeting YBX1.Cancer Biomark. 2017;18(1):1-9. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160650. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28035913
-
MicroRNA-34a and its target genes: Key factors in cancer multidrug resistance.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(7):933-9. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666151209153729. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 26648462 Review.
-
MicroRNA, SND1, and alterations in translational regulation in colon carcinogenesis.Mutat Res. 2010 Nov 10;693(1-2):94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.09.001. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20883704 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNA in cancer drug resistance: Underlying mechanisms and clinical applications.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 17;12:951864. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.951864. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36059609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the diagnostic and therapeutic roles of microRNAs in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 13;12:911856. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.911856. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications of miRNAs in drug resistance of colorectal cancer.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Aug 25;12:1758835920947342. doi: 10.1177/1758835920947342. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32922521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircDENND2A Promotes Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression via Regulating MiR-34a/CCNE1 Signaling.Front Genet. 2020 Sep 1;11:987. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00987. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33033491 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the hidden players: noncoding RNAs orchestrating polyamine metabolism in disease.Cell Biosci. 2024 Jun 25;14(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01235-3. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38918813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lubelska K., Wiktorska K., Mielczarek L., Milczarek M., Zbroinska-Bregisz I., Chilmonczyk Z. Sulforaphane regulates NFE2L2/Nrf2-dependent xenobiotic metabolism phase II and phase III enzymes differently in human colorectal cancer and untransformed epithelial colon cells. Nutrition and Cancer. 2016;68(8):1338–1348. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2016.1224369. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

