The price of progress: Funding and financing Alzheimer's disease drug development
- PMID: 30175227
- PMCID: PMC6118094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2018.04.008
The price of progress: Funding and financing Alzheimer's disease drug development
Abstract
Introduction: Advancing research and treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the search for effective treatments depend on a complex financial ecosystem involving federal, state, industry, advocacy, venture capital, and philanthropy funding approaches.
Methods: We conducted an expert review of the literature pertaining to funding and financing of translational research and drug development for AD.
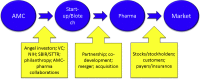
Results: The federal government is the largest public funder of research in AD. The National Institute on Aging, National Institute of Mental Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and National Center for Advancing Translational Science all fund aspects of research in AD drug development. Non-National Institutes of Health federal funding comes from the National Science Foundation, Veterans Administration, Food and Drug Administration, and the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Academic Medical Centers host much of the federally funded basic science research and are increasingly involved in drug development. Funding of the "Valley of Death" involves philanthropy and federal funding through small business programs and private equity from seed capital, angel investors, and venture capital companies. Advocacy groups fund both basic science and clinical trials. The Alzheimer Association is the advocacy organization with the largest research support portfolio relevant to AD drug development. Pharmaceutical companies are the largest supporters of biomedical research worldwide; companies are most interested in late stage de-risked drugs. Drugs progressing into phase II and III are candidates for pharmaceutical industry support through licensing, mergers and acquisitions, and co-development collaborations.
Discussion: Together, the funding and financing entities involved in supporting AD drug development comprise a complex, interactive, dynamic financial ecosystem. Funding source interaction is largely unstructured and available funding is insufficient to meet all demands for new therapies. Novel approaches to funding such as mega-funds have been proposed and more integration of component parts would assist in accelerating drug development.
Keywords: Advocacy; Alzheimer's disease; Biotechnology companies; Clinical trials; NCATS; NIGMS; NIH; NIMH; NINDS; Pharmaceutical industry; Philanthropy; SBIR; STTR; Venture capital.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer's Association 2017 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Dement. 2017;13:325–373. - PubMed
-
- Brookmeyer R., Johnson E., Ziegler-Graham K., Arrighi H.M. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2007;3:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer's Disease International . Alzheimer Disease International; London, England: 2015. World Alzheimer's Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia.
-
- Brodaty H., Heffernan M., Kochan N.A., Draper B., Trollor J.N., Reppermund S. Mild cognitive impairment in a community sample: the Sydney Memory and Ageing Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:310–317.e1. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
