Expression cloning human and rat renal cortex Na/Pi cotransporters: behind the scenes in the Murer laboratory
- PMID: 30175377
- PMCID: PMC6326002
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-018-2198-9
Expression cloning human and rat renal cortex Na/Pi cotransporters: behind the scenes in the Murer laboratory
Abstract
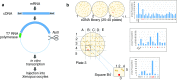
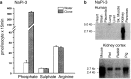
In the pre-genomic era, the cloning of a cDNA represented a significant achievement, particularly if the gene of interest encoded a membrane protein. At the time, molecular probes such as partial peptide sequences, suitable nucleic acid sequences, or antibodies were unavailable for most proteins and the "sodium-phosphate transporter" was no exception. In contrast, brush-border membrane vesicles and epithelial cell culture experiments had established a reliable set of functional hallmarks that described Na-dependent phosphate transport activity in some detail. Moreover, aspects of hormonal regulation of phosphate homeostasis could be recapitulated in these model systems. Expression cloning elegantly combined functional protein expression in Xenopus laevis oocytes with molecular biology to overcome the lack of molecular probes.
Keywords: Expression cloning; Kidney; Proximal tubule; Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter; Solute transport.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of rat sodium/phosphate cotransporters in the cell membrane transport of arsenate.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Oct 1;232(1):125-34. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.05.026. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18586044
-
Protein kinase C activators induce membrane retrieval of type II Na+-phosphate cotransporters expressed in Xenopus oocytes.J Physiol. 1999 Jun 1;517 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):327-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0327t.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10332085 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning of a rabbit renal Na-Pi cotransporter, which is regulated by dietary phosphate.Am J Physiol. 1995 Apr;268(4 Pt 2):F626-33. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.4.F626. Am J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7733319
-
Renal brush border membrane Na/Pi-cotransport: molecular aspects in PTH-dependent and dietary regulation.Kidney Int. 1996 Jun;49(6):1769-73. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.264. Kidney Int. 1996. PMID: 8743494 Review.
-
Physiological regulation of renal sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters.Jpn J Physiol. 2004 Apr;54(2):93-102. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.54.93. Jpn J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15182416 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphate transport: from microperfusion to molecular cloning.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Jan;471(1):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2245-6. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30569199 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ansermet C, Moor MB, Centeno G, Auberson M, Hu DZ, Baron R, Nikolaeva S, Haenzi B, Katanaeva N, Gautschi I, Katanaev V, Rotman S, Koesters R, Schild L, Pradervand S, Bonny O, Firsov D. Renal Fanconi syndrome and hypophosphatemic rickets in the absence of xenotropic and polytropic retroviral receptor in the nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:1073–1078. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016070726. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertran J, Werner A, Chillaron J, Nunes V, Biber J, Testar X, Zorzano A, Estivill X, Murer H, Palacin M. Expression cloning of a human renal cDNA that induces high affinity transport of L-cystine shared with dibasic amino acids in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:14842–14849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

