First Responders: Innate Immunity to Helminths
- PMID: 30177466
- PMCID: PMC6168350
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2018.08.007
First Responders: Innate Immunity to Helminths
Abstract
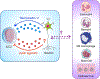
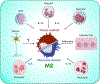
Helminth infections represent a significant public health concern resulting in devastating morbidity and economic consequences across the globe. Helminths migrate through mucosal sites causing tissue damage and the induction of type 2 immune responses. Antihelminth protection relies on the mobilization and activation of multiple immune cells, including type 2 innate lymphocytes (ILC2s), basophils, mast cells, macrophages, and hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Further, epithelial cells and neurons have been recognized as important regulators of type 2 immunity. Collectively, these pathways stimulate host-protective responses necessary for worm expulsion and the healing of affected tissues. In this review we focus on the innate immune pathways that regulate immunity to helminth parasites and describe how better understanding of these pathways may lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Mucosal Immunology; helminth parasites; innate immunity; type 2 cytokines.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization(2016) Schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiases: number of people treated in 2015. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 91 (49–50), 585–95. - PubMed
-
- Jourdan PM et al. (2017) Soil-transmitted helminth infections. Lancet. - PubMed
-
- Charlier J et al. (2014) Chasing helminths and their economic impact on farmed ruminants. Trends Parasitol 30 (7), 361–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

