Plasma gelsolin promotes re-epithelialization
- PMID: 30177722
- PMCID: PMC6120956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31441-2
Plasma gelsolin promotes re-epithelialization
Abstract
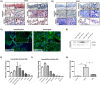
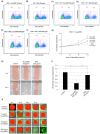
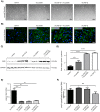
Woundhealing disorders characterized by impaired or delayed re-epithelialization are a serious medical problem that is painful and difficult to treat. Gelsolin (GSN), a known actin modulator, supports epithelial cell regeneration and apoptosis. The aim of this study was to estimate the potential of recombinant gelsolin (rhu-pGSN) for ocular surface regeneration to establish a novel therapy for delayed or complicated wound healing. We analyzed the influence of gelsolin on cell proliferation and wound healing in vitro, in vivo/ex vivo and by gene knockdown. Gelsolin is expressed in all tested tissues of the ocular system as shown by molecular analysis. The concentration of GSN is significantly increased in tear fluid samples of patients with dry eye disease. rhu-pGSN induces cell proliferation and faster wound healing in vitro as well as in vivo/ex vivo. TGF-β dependent transcription of SMA is significantly decreased after GSN gene knockdown. Gelsolin is an inherent protein of the ocular system and is secreted into the tear fluid. Our results show a positive effect on corneal cell proliferation and wound healing. Furthermore, GSN regulates the synthesis of SMA in myofibroblasts, which establishes GSN as a key protein of TGF-β dependent cell differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Drug-induced corneal damage. Prescrire Int23, 97–100 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

