Isoform-specific hyperactivation of calpain-2 occurs presymptomatically at the synapse in Alzheimer's disease mice and correlates with memory deficits in human subjects
- PMID: 30177812
- PMCID: PMC6120938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31073-6
Isoform-specific hyperactivation of calpain-2 occurs presymptomatically at the synapse in Alzheimer's disease mice and correlates with memory deficits in human subjects
Abstract
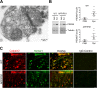
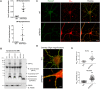
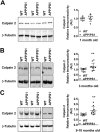
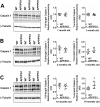
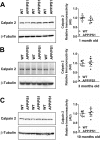
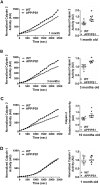
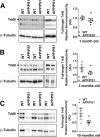
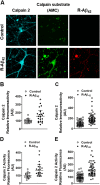
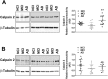
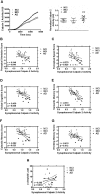
Calpain hyperactivation is implicated in late-stages of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, calpains are also critical for synaptic function and plasticity, and hence memory formation and learning. Since synaptic deficits appear early in AD pathogenesis prior to appearance of overt disease symptoms, we examined if localized dysregulation of calpain-1 and/or 2 contributes to early synaptic dysfunction in AD. Increased activity of synaptosomal calpain-2, but not calpain-1 was observed in presymptomatic 1 month old APPswe/PS1ΔE9 mice (a mouse model of AD) which have no evident pathological or behavioural hallmarks of AD and persisted up to 10 months of age. However, total cellular levels of calpain-2 remained unaffected. Moreover, synaptosomal calpain-2 was hyperactivated in frontal neocortical tissue samples of post-mortem brains of AD-dementia subjects and correlated significantly with decline in tests for cognitive and memory functions, and increase in levels of β-amyloid deposits in brain. We conclude that isoform-specific hyperactivation of calpain-2, but not calpain-1 occurs at the synapse early in the pathogenesis of AD potentially contributing to the deregulation of synaptic signaling in AD. Our findings would be important in paving the way for potential therapeutic strategies for amelioration of cognitive deficits observed in ageing-related dementia disorders like AD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aβ mediates F-actin disassembly in dendritic spines leading to cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 31;38(5):1085-1099. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2127-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29246925 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of brain magnesium prevents synaptic loss and reverses cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.Mol Brain. 2014 Sep 13;7:65. doi: 10.1186/s13041-014-0065-y. Mol Brain. 2014. PMID: 25213836 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of brain magnesium prevents and reverses cognitive deficits and synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.J Neurosci. 2013 May 8;33(19):8423-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4610-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. Retraction in: J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 16;34(16):5733. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1265-14.2014. PMID: 23658180 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The upside of APP at synapses.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Jan;18(1):47-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00221.x. Epub 2010 Dec 27. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 21199446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The synapse as a treatment avenue for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Jul;27(7):2940-2949. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01565-z. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35444256 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-dependent ataxia and neurodegeneration caused by an αII spectrin mutation with impaired regulation of its calpain sensitivity.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86470-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790315 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the Capn1 Gene Results in Alterations in Signaling Pathways Related to Alzheimer's Disease, Protein Quality Control and Synaptic Plasticity in Mouse Brain.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 9;11:334. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00334. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32328086 Free PMC article.
-
The Spread of Spectrin in Ataxia and Neurodegenerative Disease.J Exp Neurol. 2021;2(3):131-139. J Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34528024 Free PMC article.
-
The Amyloid Precursor Protein Modulates the Position and Length of the Axon Initial Segment.J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 8;43(10):1830-1844. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0172-22.2023. Epub 2023 Jan 30. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36717226 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 mediated vasoconstriction leads to memory impairment and synaptic dysfunction.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 1;11(1):4868. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84258-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649479 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

