Regulatory T cells and asthma
- PMID: 30178633
- PMCID: PMC6137416
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1700346
Regulatory T cells and asthma
Abstract
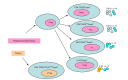
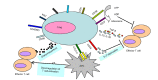
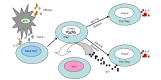
Asthma is a chronic disease of airway inflammation due to excessive T helper cell type 2 (Th2) response. Present treatment based on inhalation of synthetic glucocorticoids can only control Th2-driven chronic eosinophilic inflammation, but cannot change the immune tolerance of the body to external allergens. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are the main negative regulatory cells of the immune response. Tregs play a great role in regulating allergic, autoimmune, graft-versus-host responses, and other immune responses. In this review, we will discuss the classification and biological characteristics, the established immunomodulatory mechanisms, and the characteristics of induced differentiation of Tregs. We will also discuss the progress of Tregs in the field of asthma. We believe that further studies on the regulatory mechanisms of Tregs will provide better treatments and control strategies for asthma.
Keywords: Regulatory T cell; Asthma; Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β); Interleukin 10 (IL-10); IL-35.
Conflict of interest statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

