Transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib for the management of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30180810
- PMCID: PMC6124009
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0849-0
Transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib for the management of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the recommended treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients at Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) B-stage, whereas sorafenib is an orally administered small molecule target drug for BCLC C-stage. This updated systemic review and meta-analysis focuses on identifying the efficacy of the combination of TACE with sorafenib, which remains controversial despite years of exploration.
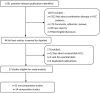
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus and the Cochrane Library were systematically reviewed to search for studies published from January 1990 to May 2017. Studies focusing on the efficacy of combination therapy for unresectable HCC were eligible. The hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) for time to progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), disease control rate (DCR) and aetiology were collected. The data were then analysed through fixed/random effects meta-analysis models with STATA 13.0. The incidence and severity of treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were also evaluated.
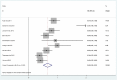
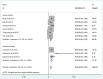
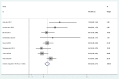
Results: Twenty-seven studies were included. Thirteen non-comparative studies reported median OS (ranging from 18.5 to 20.4 months), median TTP (ranging from 7 to 13.9 months) and DCR (ranging from 18.4 to 95%). Fourteen comparative studies provided median OS (ranging from 7.0 to 29.7 months) and median TTP (ranging from 2.6 to 10.2 months). Five comparative studies provided DCR (ranging from 32 to 97.2%). Forest plots showed that combination therapy significantly improved TTP (HR = 0.66, 95% CI 0.50-0.81, P = 0.002) rather than OS (HR = 0.63, 95% CI 0.55-0.71, P = 0.058), compared to TACE alone. DCR increased significantly in the combination therapy group (OR = 2.93, 95% CI 1.59-5.41, P = 0.005). Additional forest plots were drawn and no significant differences were observed with regard to survival outcome among various aetiologies. Forest plots for separate analysis of regions showed the HR for TTP was 0.62 (95% CI 0.45-0.79, P = 0.002) in the Asian countries group, and 0.82 (95% CI 0.59-1.05, P = 0.504)) in western countries. The HR for OS was 0.61 (95% CI 0.48-0.75, P = 0.050) in the Asian countries group and was 0.88 (95% CI 0.56-1.20, P = 0.845) in western countries. These data may indicate positive TTP outcome in Asian patients but not in European patients while no positive findings regarding OS were observed in either region. The most common AEs included fatigue, hand-foot skin reaction, diarrhoea and hypertension.
Conclusions: Combination therapy may benefit unresectable HCC patients in terms of prolonged TTP and DCR. More well-designed studies are needed to investigate its superiority for OS.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Meta-analysis; Sorafenib; Systemic review; Transarterial chemoembolization.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combination therapy of sorafenib and TACE for unresectable HCC: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 20;9(3):e91124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091124. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24651044 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Oct;41(10):6575-82. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3541-7. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25091939
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib for early or intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec;40(6):688-697. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27339594
-
Combination trans arterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus sorafenib for the management of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of the literature.Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Dec;58(12):3389-96. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2872-x. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046163
-
Yttrium-90 microsphere radioembolisation for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 16;2:CD011313. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011313.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 24;1:CD011313. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011313.pub3. PMID: 26905230 Updated.
Cited by
-
Efficiency and Stability of Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined With or Without Lenvatinib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar;35(3):212-222. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2024.23071. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39128062 Free PMC article.
-
The combination therapy of transarterial chemoembolisation and sorafenib is the preferred palliative treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Sep 11;18(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-02017-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32917226 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment by Transarterial Chemoembolization and Sorafenib for Hepatocellular Carcinoma vs Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Bangladesh: A Real-life Situation.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2019 Jul-Dec;9(2):63-66. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1300. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 32117692 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Survival of a Patient with a Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Main Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis and Spontaneous Tumor Rupture.J Liver Cancer. 2020 Sep;20(2):148-153. doi: 10.17998/jlc.20.2.148. Epub 2020 Sep 30. J Liver Cancer. 2020. PMID: 37384326 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus TACE in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Mar 31;21(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02961-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37004052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chao Y, Chung Y-H, Han G, Yoon J-H, Yang J, Wang J, Shao G-L, Kim BI, Lee T-Y. The combination of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is well tolerated and effective in Asian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Final results of the START trial. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(6):1458–1467. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29126. - DOI - PubMed
-
- EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

