The effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on serum creatinine in patients undergoing partial nephrectomy: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30180887
- PMCID: PMC6123977
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2820-3
The effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on serum creatinine in patients undergoing partial nephrectomy: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) may develop during partial nephrectomy due to ischemic reperfusion injury induced by renal artery clamping or surgical insult. The effect of remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) on reducing the renal injury after partial nephrectomy has not been evaluated in terms of urinary biomarkers.
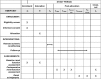
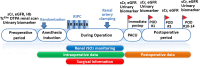
Methods/design: We will conduct a randomized controlled trial enrolling the patients who will undergo partial nephrectomy. In the study group, RIPC which consisted of four 5-min cycles of limb ischemia and reperfusion will be conducted after induction of anesthesia. Postoperative serum creatinine values, the incidence of AKI, and urinary biomarkers, including urinary creatinine, microalbumin, β-2 microglobulin, and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, will be compared between groups during the postoperative 2 weeks. Regional oxygen saturation on the skin of the contralateral kidney will be measured to evaluate the association between intraoperative regional oxygen saturation values and renal injury of the operating side.
Discussion: We expect that our trial may demonstrate the effect of RIPC on mitigating the immediate postoperative renal injury and improving patient outcomes after partial nephrectomy. Moreover, our patients will undergo 99mTc-DTPA radionuclide scintigraphy to calculate glomerular filtration rate 6 and 12 months after surgery. This data should show the long-term effect of RIPC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, ID: NCT03273751 . Registered on 6 September 2017.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Partial nephrectomy; Remote ischemic preconditioning; Urinary biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Seoul National University Institutional Review Boards (approval number: 1707–087-870, protocol version 2.1) and is registered at
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of remote ischaemic preconditioning on renal protection in patients undergoing laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: a 'blinded' randomised controlled trial.BJU Int. 2013 Jul;112(1):74-80. doi: 10.1111/bju.12004. Epub 2013 Mar 4. BJU Int. 2013. PMID: 23452148 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of differential-phase remote ischemic preconditioning intervention in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: A single blinded, randomized controlled trial in a parallel group design.J Clin Anesth. 2017 Sep;41:21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2017.05.017. Epub 2017 Jun 6. J Clin Anesth. 2017. PMID: 28802596 Clinical Trial.
-
Remote Ischemic Preconditioning To Reduce Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015 Oct;50(4):527-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 May 23. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 26015372 Clinical Trial.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning for prevention of acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Oct;64(4):574-83. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.04.029. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24954246
-
Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Outcomes in Adult Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies.Anesth Analg. 2018 Jul;127(1):30-38. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002674. Anesth Analg. 2018. PMID: 29210794
Cited by
-
Acute Kidney Injury Adjusted for Parenchymal Mass Reduction and Long-Term Renal Function after Partial Nephrectomy.J Clin Med. 2019 Sep 18;8(9):1482. doi: 10.3390/jcm8091482. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31540394 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Serum Creatinine in Patients Undergoing Partial Nephrectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 12;10(8):1636. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081636. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33921503 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin as a nephroprotector after warm ischemia: histomorphometric evaluation in a rodent model.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Jul-Aug;47(4):796-802. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0358. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33848072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaspar A, Pereira MA, Azevedo P, Lourenco A, Marques J, Leite-Moreira A. Remote ischemic conditioning in ST-elevation myocardial infarction as adjuvant to primary angioplasty (RIC-STEMI): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:398. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0937-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

