The role of α-ketoglutarate-dependent proteins in pluripotency acquisition and maintenance
- PMID: 30181211
- PMCID: PMC6462505
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.000831
The role of α-ketoglutarate-dependent proteins in pluripotency acquisition and maintenance
Abstract
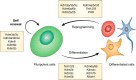
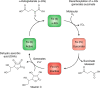
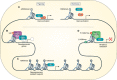
α-Ketoglutarate is an important metabolic intermediate that acts as a cofactor for several chromatin-modifying enzymes, including histone demethylases and the Tet family of enzymes that are involved in DNA demethylation. In this review, we focus on the function and genomic localization of these α-ketoglutarate-dependent enzymes in the maintenance of pluripotency during cellular reprogramming to induced pluripotent stem cells and in disruption of pluripotency during in vitro differentiation. The enzymatic function of many of these α-ketoglutarate-dependent proteins is required for pluripotency acquisition and maintenance. A better understanding of their specific function will be essential in furthering our knowledge of pluripotency.
Keywords: DNA demethylation; cell differentiation; cell fate; chromatin; epigenetics; histone demethylase; induced pluripotent stem cell (iPS cell) (iPSC); pluripotency; reprogramming; stem cells; α-KG enzymes.
© 2019 Tran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
AKT signaling is associated with epigenetic reprogramming via the upregulation of TET and its cofactor, alpha-ketoglutarate during iPSC generation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Sep 25;12(1):510. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02578-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34563253 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Opening Modulates Histone Lysine Methylation at the Early Phase of Somatic Cell Reprogramming.Cell Metab. 2018 Dec 4;28(6):935-945.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Cell Metab. 2018. PMID: 30174306
-
Histone demethylase KDM6A promotes somatic cell reprogramming by epigenetically regulating the PTEN and IL-6 signal pathways.Stem Cells. 2020 Aug;38(8):960-972. doi: 10.1002/stem.3188. Epub 2020 May 5. Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32346926
-
LSD1: Expanding Functions in Stem Cells and Differentiation.Cells. 2021 Nov 20;10(11):3252. doi: 10.3390/cells10113252. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of cellular reprogramming to induced pluripotency.Epigenomics. 2016 Aug;8(8):1131-49. doi: 10.2217/epi-2016-0032. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Epigenomics. 2016. PMID: 27419933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resolving Geroplasticity to the Balance of Rejuvenins and Geriatrins.Aging Dis. 2022 Dec 1;13(6):1664-1714. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0414. eCollection 2022 Dec 1. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 36465174 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming: identifying the mechanisms that safeguard cell identity.Development. 2019 Dec 2;146(23):dev182170. doi: 10.1242/dev.182170. Development. 2019. PMID: 31792064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal 1-Nitropyrene Exposure Causes Autism-Like Behavior Partially by Altering DNA Hydroxymethylation in Developing Brain.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jul;11(28):e2306294. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306294. Epub 2024 May 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38757379 Free PMC article.
-
Brain development and bioenergetic changes.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Sep;199:106550. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106550. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38849103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamine Metabolism and Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 18;16(16):2871. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162871. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernstein B. E., Mikkelsen T. S., Xie X., Kamal M., Huebert D. J., Cuff J., Fry B., Meissner A., Wernig M., Plath K., Jaenisch R., Wagschal A., Feil R., Schreiber S. L., and Lander E. S. (2006) A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell 125, 315–326 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.041 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu J., Vodyanik M. A., Smuga-Otto K., Antosiewicz-Bourget J., Frane J. L., Tian S., Nie J., Jonsdottir G. A., Ruotti V., Stewart R., Slukvin I. I., and Thomson J. A. (2007) Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 318, 1917–1920 10.1126/science.1151526 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

