Crebbp Loss Drives Small Cell Lung Cancer and Increases Sensitivity to HDAC Inhibition
- PMID: 30181244
- PMCID: PMC6294438
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0385
Crebbp Loss Drives Small Cell Lung Cancer and Increases Sensitivity to HDAC Inhibition
Abstract
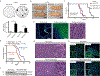
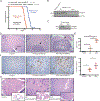
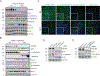
CREBBP, encoding an acetyltransferase, is among the most frequently mutated genes in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), a deadly neuroendocrine tumor type. We report acceleration of SCLC upon Crebbp inactivation in an autochthonous mouse model. Extending these observations beyond the lung, broad Crebbp deletion in mouse neuroendocrine cells cooperated with Rb1/Trp53 loss to promote neuroendocrine thyroid and pituitary carcinomas. Gene expression analyses showed that Crebbp loss results in reduced expression of tight junction and cell adhesion genes, including Cdh1, across neuroendocrine tumor types, whereas suppression of Cdh1 promoted transformation in SCLC. CDH1 and other adhesion genes exhibited reduced histone acetylation with Crebbp inactivation. Treatment with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor Pracinostat increased histone acetylation and restored CDH1 expression. In addition, a subset of Rb1/Trp53/Crebbp-deficient SCLC exhibited exceptional responses to Pracinostat in vivo Thus, CREBBP acts as a potent tumor suppressor in SCLC, and inactivation of CREBBP enhances responses to a targeted therapy.Significance: Our findings demonstrate that CREBBP loss in SCLC reduces histone acetylation and transcription of cellular adhesion genes, while driving tumorigenesis. These effects can be partially restored by HDAC inhibition, which exhibited enhanced effectiveness in Crebbp-deleted tumors. These data provide a rationale for selectively treating CREBBP-mutant SCLC with HDAC inhibitors. Cancer Discov; 8(11); 1422-37. ©2018 AACR. This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1333.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The dual HDAC-PI3K inhibitor CUDC-907 displays single-agent activity and synergizes with PARP inhibitor olaparib in small cell lung cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 17;39(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01728-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33069237 Free PMC article.
-
Cell of origin of small cell lung cancer: inactivation of Trp53 and Rb1 in distinct cell types of adult mouse lung.Cancer Cell. 2011 Jun 14;19(6):754-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.04.019. Cancer Cell. 2011. PMID: 21665149
-
Loss of p130 accelerates tumor development in a mouse model for human small-cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2010 May 15;70(10):3877-83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4228. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20406986 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in regulating cell proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance and their applications as cancer biomarkers in small cell lung cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Aug;1876(1):188552. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188552. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33892053 Review.
-
Small cell lung cancer, an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like cancer: significance of inactive Notch signaling and expression of achaete-scute complex homologue 1.Hum Cell. 2017 Jan;30(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s13577-016-0149-3. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Hum Cell. 2017. PMID: 27785690 Review.
Cited by
-
The Synergistic Effects of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid and Vorinostat in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 21;12:625543. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.625543. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34093178 Free PMC article.
-
KIX domain determines a selective tumor-promoting role for EP300 and its vulnerability in small cell lung cancer.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 18;8(7):eabl4618. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4618. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35171684 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA CREBBP Suppresses Hepatic Fibrosis Via Targeting the hsa-miR-1291/LEFTY2 Axis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 22;12:741151. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.741151. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34887753 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Precision Medicine Identifies New Therapeutic Candidates for Medulloblastoma.Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;80(23):5393-5407. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1655. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33046443 Free PMC article.
-
Small cell lung cancer: emerging subtypes, signaling pathways, and therapeutic vulnerabilities.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Aug 5;13(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00548-w. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39103941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- George J, Lim JS, Jang SJ, Cun Y, Ozretic L, Kong G, et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015;524(7563):47–53 doi 10.1038/nature14664. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rudin CM, Durinck S, Stawiski EW, Poirier JT, Modrusan Z, Shames DS, et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies SOX2 as a frequently amplified gene in small-cell lung cancer. Nature genetics 2012. doi 10.1038/ng.2405. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Augert A, Zhang Q, Bates B, Cui M, Wang X, Wildey G, et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer Exhibits Frequent Inactivating Mutations in the Histone Methyltransferase KMT2D/MLL2: CALGB 151111 (Alliance). Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2017;12(4):704–13 doi 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.12.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gazdar AF, Bunn PA, Minna JD. Small-cell lung cancer: what we know, what we need to know and the path forward. Nature reviews Cancer 2017;17(12):725–37 doi 10.1038/nrc.2017.87. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zehir A, Benayed R, Shah RH, Syed A, Middha S, Kim HR, et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat Med 2017;23(6):703–13 doi 10.1038/nm.4333. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

