A Capillary Computing Architecture for Dynamic Internet of Things: Orchestration of Microservices from Edge Devices to Fog and Cloud Providers
- PMID: 30181454
- PMCID: PMC6164252
- DOI: 10.3390/s18092938
A Capillary Computing Architecture for Dynamic Internet of Things: Orchestration of Microservices from Edge Devices to Fog and Cloud Providers
Abstract
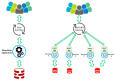
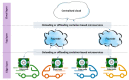
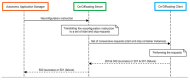
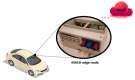
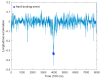
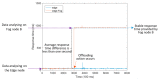
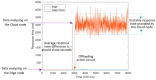
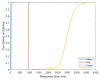
The adoption of advanced Internet of Things (IoT) technologies has impressively improved in recent years by placing such services at the extreme Edge of the network. There are, however, specific Quality of Service (QoS) trade-offs that must be considered, particularly in situations when workloads vary over time or when IoT devices are dynamically changing their geographic position. This article proposes an innovative capillary computing architecture, which benefits from mainstream Fog and Cloud computing approaches and relies on a set of new services, including an Edge/Fog/Cloud Monitoring System and a Capillary Container Orchestrator. All necessary Microservices are implemented as Docker containers, and their orchestration is performed from the Edge computing nodes up to Fog and Cloud servers in the geographic vicinity of moving IoT devices. A car equipped with a Motorhome Artificial Intelligence Communication Hardware (MACH) system as an Edge node connected to several Fog and Cloud computing servers was used for testing. Compared to using a fixed centralized Cloud provider, the service response time provided by our proposed capillary computing architecture was almost four times faster according to the 99th percentile value along with a significantly smaller standard deviation, which represents a high QoS.
Keywords: Edge computing; Fog computing; Internet of Things; Microservices; container-based virtualization; on/offloading.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Smart Containers Schedulers for Microservices Provision in Cloud-Fog-IoT Networks. Challenges and Opportunities.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 19;20(6):1714. doi: 10.3390/s20061714. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32204390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Scheduling of Contextually Categorised Internet of Things Services in Fog Computing Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 8;22(2):465. doi: 10.3390/s22020465. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062426 Free PMC article.
-
AI augmented edge and fog computing for Internet of Health Things (IoHT).PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Jan 30;11:e2431. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2431. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40062251 Free PMC article.
-
Fog Computing and Edge Computing Architectures for Processing Data From Diabetes Devices Connected to the Medical Internet of Things.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017 Jul;11(4):647-652. doi: 10.1177/1932296817717007. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017. PMID: 28745086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Multi-Classifiers Based Algorithm for Energy Efficient Tasks Offloading in Fog Computing.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 16;23(16):7209. doi: 10.3390/s23167209. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631746 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fuzzy-Based Microservice Resource Management Platform for Edge Computing in the Internet of Things.Sensors (Basel). 2021 May 31;21(11):3800. doi: 10.3390/s21113800. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072637 Free PMC article.
-
A Data-driven Adaptive Sampling Method Based on Edge Computing.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Apr 12;20(8):2174. doi: 10.3390/s20082174. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32290534 Free PMC article.
-
A Perceptive Interface for Intelligent Cyber Enterprises.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 12;19(20):4422. doi: 10.3390/s19204422. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614821 Free PMC article.
-
An Intelligent Individualized Cardiovascular App for Risk Elimination (iCARE) for Individuals With Coronary Heart Disease: Development and Usability Testing Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021 Dec 13;9(12):e26439. doi: 10.2196/26439. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2021. PMID: 34898449 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling the Orchestration of IoT Slices through Edge and Cloud Microservice Platforms.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jul 5;19(13):2980. doi: 10.3390/s19132980. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31284514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taherizadeh S., Jones A., Taylor I., Zhao Z., Stankovski V. Monitoring self-adaptive applications within edge computing frameworks: A state-of-the-art review. J. Syst. Softw. 2018;136:19–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.10.033. - DOI
-
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B. [(accessed on 8 August 2018)]; Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-3-model-b/
-
- Arduino. [(accessed on 8 August 2018)]; Available online: https://www.arduino.cc/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

