Novel Whole-Cell Inactivated Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Microparticles as Vaccine Formulation in Microneedle-Based Transdermal Immunization
- PMID: 30181504
- PMCID: PMC6161099
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines6030060
Novel Whole-Cell Inactivated Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Microparticles as Vaccine Formulation in Microneedle-Based Transdermal Immunization
Abstract
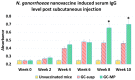
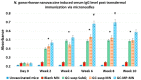
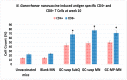
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a strict human pathogen responsible for more than 100 million new sexually transmitted infections worldwide each year. Due to the global emergence of antibiotic resistance, the Center for Disease control (CDC) recently listed N. gonorrhoeae as an urgent threat to public health. No vaccine is available in spite of the huge disease burden and the possibility of untreatable gonorrhea. The aim of this study is to investigate the immunogenicity of a novel whole-cell-based inactivated gonococcal microparticle vaccine formulation loaded in dissolvable microneedles for transdermal administration. The nanotechnology-based vaccine formulation consists of inactivated whole-cell gonococci strain CDC-F62, spray dried and encapsulated into biodegradable cross-linked albumin matrix with sustained slow antigen release. The dry vaccine nanoparticles were then loaded in a dissolvable microneedle skin patch for transdermal delivery. The efficacy of the whole-cell microparticles vaccine formulation loaded in microneedles was assessed in vitro using dendritic cells and macrophages as well as in vivo mouse model. Antibody titers were measured using an enzyme immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and antigen-specific T lymphocytes were assessed in spleens and lymph nodes. Here we report that whole-cell-based gonococcal microparticle vaccine loaded in dissolvable microneedles for transdermal administration induced significant increase in antigen-specific IgG antibody titers and antigen-specific CD4 and CD8 T lymphocytes in mice compared to gonococcal antigens in solution or empty microneedles. Significant increase in antigen-specific IgG antibody levels was observed at the end of week 2 in groups that received the vaccine compared to the group receiving empty nanoparticles. The advantages of using formalin-fixed whole-cell gonococci that all immunogenic epitopes are covered and preserved from degradation. The spherical shaped micro and nanoparticles are biological mimics of gonococci, therefore present to the immune system as invaders but without the ability to suppress adaptive immunity. In conclusion, the transdermal delivery of microparticles vaccine via a microneedle patch was shown to be an effective system for vaccine delivery. The novel gonorrhea nanovaccine is cheap to produce in a stable dry powder and can be delivered in microneedle skin patch obviating the need for needle use or the cold chain.
Keywords: Neisseria gonorrhoeae; antigen-specific CD4 T lymphocytes; antigen-specific antibody; gonorrhea; microneedle; nanotechnology; skin patch; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gonococcal microparticle vaccine in dissolving microneedles induced immunity and enhanced bacterial clearance in infected mice.Int J Pharm. 2023 Jul 25;642:123182. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123182. Epub 2023 Jun 25. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37369287 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of In Vitro Immunostimulatory Activity of an Adjuvanted Whole-Cell Inactivated Neisseria gonorrhoeae Microparticle Vaccine Formulation.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 21;10(7):983. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10070983. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35891147 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of PLGA-Loaded Influenza Vaccine Microparticles Using Dissolving Microneedles Induces a Robust Immune Response.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 12;17(4):510. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040510. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284505 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedles: A New Generation Vaccine Delivery System.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;12(4):435. doi: 10.3390/mi12040435. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle Patches as Drug and Vaccine Delivery Platform.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(22):2413-2422. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170526124053. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28552053 Review.
Cited by
-
Addressing Sexually Transmitted Infections Due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the Present and Future.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 28;12(5):884. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050884. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart Microneedles for Therapy and Diagnosis.Research (Wash D C). 2020 Dec 18;2020:7462915. doi: 10.34133/2020/7462915. eCollection 2020. Research (Wash D C). 2020. PMID: 33623910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissolvable Microneedle Patches to Enable Increased Access to Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and Future Pandemic Outbreaks.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Apr 1;9(4):320. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9040320. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33915696 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobiosystems for Antimicrobial Drug-Resistant Infections.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;11(5):1075. doi: 10.3390/nano11051075. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 25;24(13):10612. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310612. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. [(accessed on 19 October 2016)];2013 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/index.html.
-
- Kirkcaldy R.D., Harvey A., Papp J.R., del Rio C., Soge O.O., Holmes K.K., Hook E.W., III, Kubin G., Riedel S., Zenilman J., et al. Neisseria gonorrhoeae antimicrobial susceptibility surveillance—The gonococcal isolate surveillance project, 27 sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2016;65:1–19. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6507a1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- STD Rates Reach Record High in United States. [(accessed on 20 October 2016)]; Available online: http://www.cnn.com/2016/10/20/health/std-statistics-record-high/index.html.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

