Pixantrone, a new anticancer drug with the same old cardiac problems? An in vitro study with differentiated and non-differentiated H9c2 cells
- PMID: 30181708
- PMCID: PMC6117818
- DOI: 10.2478/intox-2018-0002
Pixantrone, a new anticancer drug with the same old cardiac problems? An in vitro study with differentiated and non-differentiated H9c2 cells
Abstract
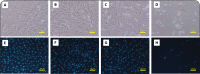
Pixantrone (PIX) is an anticancer drug approved for the treatment of multiple relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is an aza-anthracenedione synthesized to have the same anticancer activity as its predecessors, anthracyclines (e.g. doxorubicin) and anthracenediones (e.g. mitoxantrone), with lower cardiotoxicity. However, published data regarding its possible cardiotoxicity are scarce. Therefore, this work aimed to assess the potential cytotoxicity of PIX, at clinically relevant concentrations (0.1; 1; and 10 μM) in both non-differentiated and 7-day differentiated H9c2 cells. Cells were exposed to PIX for 48 h and cytotoxicity was evaluated through phase contrast microscopy, Hoescht staining and the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction and neutral red (NR) uptake assays. Cytotoxicity was observed in differentiated and non-differentiated H9c2 cells, with detached cells and round cells evidenced by phase contrast microscopy, mainly at the highest concentration tested (10 μM). In the Hoechst staining, PIX 10 μM showed a marked decrease in the number of cells when compared to control but with no signs of nuclear condensation. Furthermore, significant concentration-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction was observed through the MTT reduction assay. The NR assay showed similar results to those obtained in the MTT reduction assay in both differentiated and non-differentiated H9c2 cells. The differentiation state of the cells was not crucial to PIX effects, although PIX toxicity was slightly higher in differentiated H9c2 cells. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first in vitro study performed with PIX in H9c2 cells and it discloses worrying cytotoxicity at clinically relevant concentrations.
Keywords: H9c2 cells; Pixantrone; cardiotoxicity.
Figures

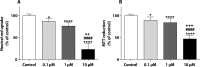

Similar articles
-
Doxorubicin Is Key for the Cardiotoxicity of FAC (5-Fluorouracil + Adriamycin + Cyclophosphamide) Combination in Differentiated H9c2 Cells.Biomolecules. 2019 Jan 10;9(1):21. doi: 10.3390/biom9010021. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30634681 Free PMC article.
-
The Main Metabolites of Fluorouracil + Adriamycin + Cyclophosphamide (FAC) Are Not Major Contributors to FAC Toxicity in H9c2 Cardiac Differentiated Cells.Biomolecules. 2019 Mar 11;9(3):98. doi: 10.3390/biom9030098. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30862114 Free PMC article.
-
Naphthoquinoxaline metabolite of mitoxantrone is less cardiotoxic than the parent compound and it can be a more cardiosafe drug in anticancer therapy.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Apr;91(4):1871-1890. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1839-z. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27629428
-
Pixantrone: novel mode of action and clinical readouts.Expert Rev Hematol. 2018 Jul;11(7):587-596. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2018.1476848. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Expert Rev Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29912583 Review.
-
Pixantrone maleate for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2009 Nov;45(11):797-805. doi: 10.1358/dot.2009.45.11.1438459. Drugs Today (Barc). 2009. PMID: 20126672 Review.
Cited by
-
Endophytic fungi: A treasure trove of novel anticancer compounds.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Sep 1;2:100050. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100050. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beggiolin G, Crippa L, Menta E, Manzotti C, Cavalletti E, Pezzoni G, Torriani D, Randisi E, Cavagnoli R, Sala F, Giuliani FC, Spinelli S. Bbr 2778, an aza-anthracenedione endowed with preclinical anticancer activity and lack of delayed cardiotoxicity. Tumori. 2001;87:407–416. - PubMed
-
- Borchmann P, Morschhauser F, Parry A, Schnell R, Harousseau JL, Gisselbrecht C, Rudolph C, Wilhelm M, Gunther H, Pfreundschuh DM, Camboni G, Engert A. Phase-II study of the new aza-anthracenedione, BBR 2778, in patients with relapsed aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Haematologica. 2003;88:888–894. - PubMed
-
- Capranico G, Tinelli S, Austin CA, Fisher ML, Zunino F. Different patterns of gene expression of topoisomerase II isoforms in differentiated tissues during murine development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1132:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Cavalletti E, Crippa L, Mainardi P, Oggioni N, Cavagnoli R, Bellini O, Sala F. Pixantrone (BBR 2778) has reduced cardiotoxic potential in mice pretreated with doxorubicin: comparative studies against doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. Invest New Drugs. 2007;25:187–195. - PubMed
-
- Conner CS. Mitoxantrone: a replacement for doxorubicin? Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1984;18:479–480. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
