Sonoporation by microbubbles as gene therapy approach against liver cancer
- PMID: 30181808
- PMCID: PMC6114955
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25875
Sonoporation by microbubbles as gene therapy approach against liver cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Sonoporation by microbubbles as gene therapy approach against liver cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 30;9(85):35600. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26305. eCollection 2018 Oct 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30473755 Free PMC article.
Abstract
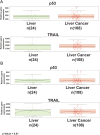
Introduction: An innovative method, known as sonoporation, was used to induce the expression of silenced genes, such as (but not restricted to) TRAIL and p53, in liver cancer cells (HepG2). The principal aim of the present study was the re-activation of silenced apoptotic pathways in liver cancer models, by using diagnostic synovial microbubble as plasmid gene delivery tools in combination with epigenetic treatments.
Material and methods: HepG2 cells were used as a liver cancer model. Microbubbles (Sonovue®) were chosen as gene deliver system in combination with the sonoporation approach. Plasmid pEGFP-TRAIL and pEGFP-p53 were selected and propagated in Escherichia coli grown in LB broth, in order to obtain the necessary amount.
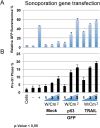
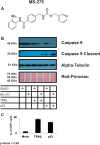
Results: Sonoporation was induced by using transducer (Sonitron 2000) and, among the several conditions tested, 3 MHz, 51% Duty Cycle, and 5 W/cm2, 30 s resulted as the best parameters. Data collected showed a dose dependent effect in terms of output energy. A transfection efficacy of 30 - 50% was achieved and recombinant gene expression induced apoptotic effects. In order to increase efficacy, we used the histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi, entinostat) MS-275, able to activate TRAIL and thus inducing a stronger pro-apoptotic effect in combination with TRAIL-gene re-expression.
Conclusion: For the first time, it was shown the possibility to induce the exogenous expression of the pro-apoptotic gene TRAIL and p53 in a liver cancer HepG2 cells via a sonoporation procedure. The epigenetic treatment using HDACi was able to increase the pro-apoptotic effects of the gene therapy.
Keywords: gene therapy; liver cancer; microbubbles; sonoporation; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chung YE, Kim KW. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography: advance and current status inabdominal imaging. Ultrasonography. 2015;34:3–18. https://doi.org/10.14366/usg.14034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leen E, Angerson WJ, Yarmenitis S, Bongartz G, Blomley M, Del Maschio A, Summaria V, Maresca G, Pezzoli C, Llull JB. Multi-centre clinical study evaluating the efficacy of SonoVue (BR1), a new ultrasound contrast agent in Doppler investigation of focal hepatic lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2002;41:200–6. doi: 10.1016/S0720-048X(01)00457-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mullick Chowdhury S, Lee T, Willmann JK. Ultrasound-guided drug delivery in cancer. Ultrasonography. 2017;36:171–84. https://doi.org/10.14366/usg.17021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koczera P, Appold L, Shi Y, Liu M, Dasgupta A, Pathak V, Ojha T, Fokong S, Wu Z, van Zandvoort M, Iranzo O, Kuehne AJC, Pich A, et al. PBCA-based polymeric microbubbles for molecular imaging and drug delivery. J Control Release. 2017;259:128–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

