The Hippo Signaling Network and Its Biological Functions
- PMID: 30183404
- PMCID: PMC6322405
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031621
The Hippo Signaling Network and Its Biological Functions
Abstract
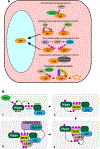
Hippo signaling is an evolutionarily conserved network that has a central role in regulating cell proliferation and cell fate to control organ growth and regeneration. It promotes activation of the LATS kinases, which control gene expression by inhibiting the activity of the transcriptional coactivator proteins YAP and TAZ in mammals and Yorkie in Drosophila. Diverse upstream inputs, including both biochemical cues and biomechanical cues, regulate Hippo signaling and enable it to have a key role as a sensor of cells' physical environment and an integrator of growth control signals. Several components of this pathway localize to cell-cell junctions and contribute to regulation of Hippo signaling by cell polarity, cell contacts, and the cytoskeleton. Downregulation of Hippo signaling promotes uncontrolled cell proliferation, impairs differentiation, and is associated with cancer. We review the current understanding of Hippo signaling and highlight progress in the elucidation of its regulatory mechanisms and biological functions.
Keywords: Hippo; YAP; Yorkie; cancer; growth.
Figures
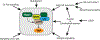
Similar articles
-
Hippo signaling promotes JNK-dependent cell migration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 21;114(8):1934-1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1621359114. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28174264 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo-Yap/Taz signaling: Complex network interactions and impact in epithelial cell behavior.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020 May;9(3):e371. doi: 10.1002/wdev.371. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31828974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals.Cell. 2007 Sep 21;130(6):1120-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.019. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17889654 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual regulation between Hippo signaling and actin cytoskeleton.Protein Cell. 2013 Dec;4(12):904-10. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-3084-z. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 24248471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD by p38 MAPK-induced cytoplasmic translocation.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Jul 28;19(8):996-1002. doi: 10.1038/ncb3581. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28752853 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Increasing kinase domain proximity promotes MST2 autophosphorylation during Hippo signaling.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 20;295(47):16166-16179. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015723. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32994222 Free PMC article.
-
DRP1: At the Crossroads of Dysregulated Mitochondrial Dynamics and Altered Cell Signaling in Cancer Cells.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 17;8(48):45208-45223. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06547. eCollection 2023 Dec 5. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38075775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaggy regulates tissue growth through Hippo pathway in Drosophila.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Nov;65(11):2131-2144. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2156-2. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36057002
-
Mechanical and metabolic interplay in the brain metastatic microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 18;12:932285. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.932285. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36059679 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Feb 19;17:1105-1120. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S444758. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38406325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler JJ, Johnson DE, Heller BL, Bringman LR, Ranahan WP, et al. 2013. Serum deprivation inhibits the transcriptional co-activator YAP and cell growth via phosphorylation of the 130-kDa isoform of Angiomotin by the LATS1/2 protein kinases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110:17368–73 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, et al. 2013. A Mechanical Checkpoint Controls Multicellular Growth through YAP/TAZ Regulation by Actin-Processing Factors. Cell 154:1047–59 - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner R, Pörnbacher I, Buser N, Hafen E, Stocker H. 2010. The WW domain protein Kibra acts upstream of Hippo in Drosophila. Dev Cell 18:309–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

