The Putative Smallest Introns in the Arabidopsis Genome
- PMID: 30184083
- PMCID: PMC6161759
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evy197
The Putative Smallest Introns in the Arabidopsis Genome
Abstract
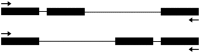
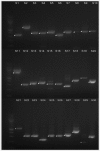
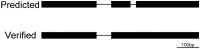
Most eukaryotic genes contain introns, which are noncoding sequences that are removed during premRNA processing. Introns are usually preserved across evolutionary time. However, the sizes of introns vary greatly. In Arabidopsis, some introns are longer than 10 kilo base pairs (bp) and others are predicted to be shorter than 10 bp. To identify the shortest intron in the genome, we analyzed the predicted introns in annotated version 10 of the Arabidopsis thaliana genome and found 103 predicted introns that are 30 bp or shorter, which make up only 0.08% of all introns in the genome. However, our own bioinformatics and experimental analyses found no evidence for the existence of these predicted introns. The predicted introns of 30-39 bp, 40-49 bp, and 50-59 bp in length are also rare and constitute only 0.07%, 0.2%, and 0.28% of all introns in the genome, respectively. An analysis of 30 predicted introns 31-59 bp long verified two in this range, both of which were 59 bp long. Thus, this study suggests that there is a limit to how small introns in A. thaliana can be, which is useful for the understanding of the evolution and processing of small introns in plants in general.
Figures


References
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative 2000. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408(6814):796–815. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MD, Leitch IJ, Price HJ, Johnston JS.. 2003. Comparisons with Caenorhabditis (approximately 100 Mb) and Drosophila (approximately 175 Mb) using flow cytometry show genome size in Arabidopsis to be approximately 157 Mb and thus approximately 25% larger than the Arabidopsis genome initiative estimate of approximately 125 Mb. Ann Bot. 91(5):547–557. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bulman S, Ridgway HJ, Eady C, Conner AJ.. 2007. Intron-rich gene structure in the intracellular plant parasite Plasmodiophora brassicae. Protist 158(4):423–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

