Reversal of albuminuria by combined AM6545 and perindopril therapy in experimental diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 30184259
- PMCID: PMC6240130
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14495
Reversal of albuminuria by combined AM6545 and perindopril therapy in experimental diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
Background and purpose: The endocannabinoid (EC) system has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy (DN). We investigated the effects of peripheral blockade of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor as an add-on treatment to ACE-inhibition in type 1 diabetic mice (DM) with established albuminuria.
Experimental approach: Renal functional parameters (albumin excretion rate, creatinine clearance), tubular injury, renal structure, both EC and CB receptor levels and markers of podocyte dysfunction, fibrosis and inflammation were studied in streptozotocin-induced DM treated for 14 weeks with vehicle, the ACE-inhibitor perindopril (2 mg·kg-1 ·day-1 ), peripherally-restricted CB1 receptor antagonist AM6545 (10 mg·kg-1 ·day-1 ) or both. Treatments began at 8 weeks after diabetes onset, when early DN is established.
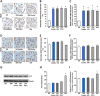
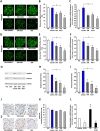
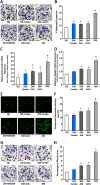
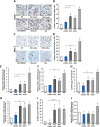
Key results: CB1 receptors were overexpressed in DM and neither perindopril nor AM6545 altered this effect, while both drugs abolished diabetes-induced overexpression of angiotensin AT1 receptors. Single treatment with either AM6545 or perindopril significantly reduced progression of albuminuria, down-regulation of nephrin and podocin, inflammation and expression of markers of fibrosis. However, reversal of albuminuria was only observed in mice administered both treatments. The ability of the combination therapy to completely abolish slit diaphragm protein loss, monocyte infiltration, overexpression of inflammatory markers and favour macrophage polarization towards an M2 phenotype may explain this greater efficacy. In vitro experiments confirmed that CB1 receptor activation directly inhibits retinoic acid-induced nephrin expression in podocytes and IL-4-induced M2 polarization in macrophages.
Conclusion and implications: Peripheral CB1 receptor blockade used as add-on treatment to ACE-inhibition reverses albuminuria, nephrin loss and inflammation in DM.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual therapy targeting the endocannabinoid system prevents experimental diabetic nephropathy.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Oct 1;32(10):1655-1665. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx010. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28387811
-
Cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade ameliorates albuminuria in experimental diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes. 2010 Apr;59(4):1046-54. doi: 10.2337/db09-1336. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20068137 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid-1 receptor deletion in podocytes mitigates both glomerular and tubular dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Mar;20(3):698-708. doi: 10.1111/dom.13150. Epub 2017 Dec 3. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29106063
-
Perindopril treatment in streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropaty.Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2013;34(1):99-108. Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 2013. PMID: 23928803
-
Renal protection and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in microalbuminuric type I and type II diabetic patients.J Hypertens Suppl. 1996 Dec;14(6):S11-4. J Hypertens Suppl. 1996. PMID: 9023709 Review.
Cited by
-
The intervention of cannabinoid receptor in chronic and acute kidney disease animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Feb 15;16(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01283-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38360685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 (CB1) as a Molecular Target for Modulating Body Weight in Man.Molecules. 2021 Oct 13;26(20):6178. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206178. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Inhibition in Chronic Kidney Disease: A New Therapeutic Toolbox.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 7;12:720734. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.720734. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34305821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Lebanese Cannabis Oil Extract in the Management of Sodium Orthovanadate-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 27;26(9):4142. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094142. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362381 Free PMC article.
-
Goods and Bads of the Endocannabinoid System as a Therapeutic Target: Lessons Learned after 30 Years.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Sep;75(5):885-958. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000600. Epub 2023 May 10. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37164640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barutta F, Bruno G, Grimaldi S, Gruden G (2015). Inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: moving toward clinical biomarkers and targets for treatment. Endocrine 48: 730–742. - PubMed
-
- Barutta F, Grimaldi S, Franco I, Bellini S, Gambino R, Pinach S et al (2014). Deficiency of cannabinoid receptor of type 2 worsens renal functional and structural abnormalities in streptozotocin‐induced diabetic mice. Kidney Int 86: 979–990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

