Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 30185178
- PMCID: PMC6125866
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-018-0268-4
Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: IL-6 classic signaling is linked to anti-inflammatory functions while the trans-signaling is associated with pro-inflammatory responses. Classic signaling is induced via membrane-bound IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) whereas trans-signaling requires prior binding of IL-6 to the soluble IL-6R. In both cases, association with the signal transducing gp130 receptor is compulsory. However, differences in the downstream signaling mechanisms of IL-6 classic- versus trans-signaling remains largely elusive.
Methods: In this study, we used flow cytometry, quantitative PCR, ELISA and immuno-blotting techniques to investigate IL-6 classic and trans-signaling mechanisms in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs).
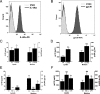
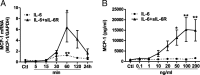
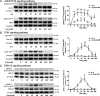
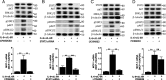
Results: We show that both IL-6R and gp130 are expressed on the surface of human vascular endothelial cells, and that the expression is affected by pro-inflammatory stimuli. In contrast to IL-6 classic signaling, IL-6 trans-signaling induces the release of the pro-inflammatory chemokine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) from human vascular endothelial cells. In addition, we reveal that the classic signaling induces activation of the JAK/STAT3 pathway while trans-signaling also activates the PI3K/AKT and the MEK/ERK pathways. Furthermore, we demonstrate that MCP-1 induction by IL-6 trans-signaling requires simultaneous activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways.
Conclusions: Collectively, our study reports molecular differences in IL-6 classic- and trans-signaling in human vascular endothelial cells; and elucidates the pathways which mediate MCP-1 induction by IL-6 trans-signaling.
Keywords: Endothelium; HUVECs; Interleukin-6 signaling; Monocyte chemoattractant Protein-1; Pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the IL-6 classic- and trans-signaling pathways in corneal sterile inflammation and wound healing.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Nov 1;52(12):8549-57. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7956. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21989726
-
Neuroprotection of interleukin-6 against NMDA-induced neurotoxicity is mediated by JAK/STAT3, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Mar;33(2):241-51. doi: 10.1007/s10571-012-9891-6. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23161148 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 induced by IFN-γ from tumor-associated macrophages via the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways promoted progression of lung cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;22(6):1026-1033. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1161-7. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28748356
-
Interleukin-6: A Masterplayer in the Cytokine Network.Oncology. 2020;98(3):131-137. doi: 10.1159/000505099. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Oncology. 2020. PMID: 31958792 Review.
-
The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: recent advances towards specific inhibition.Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Jun;34:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25749511 Review.
Cited by
-
CPEB3 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by disrupting the crosstalk between colorectal cancer cells and tumor-associated macrophages via IL-6R/STAT3 signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 11;39(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01637-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32653013 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor and Anti-Invasive Effect of Apigenin on Human Breast Carcinoma through Suppression of IL-6 Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 27;20(13):3143. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133143. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31252615 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K-AKT activation resculpts integrin signaling to drive filamentous tau-induced proinflammatory astrogliosis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 23:rs.3.rs-3253118. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3253118/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Cell Biosci. 2023 Sep 27;13(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01128-x. PMID: 37674732 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
NKX2‑1 copy number alterations are associated with oncogenic, immunological and prognostic remodeling in non‑small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2024 May 8;28(1):303. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14436. eCollection 2024 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38774453 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 6 regulates the expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 in thyroid cancer.Cancer Sci. 2021 Mar;112(3):997-1010. doi: 10.1111/cas.14752. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33247999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suzuki M, Hashizume M, Yoshida H, Mihara M. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6R antibody: effect on the expression of chemokine and adhesion molecule. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30:309–15. 10.1007/s00296-009-0953-0. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

