Effect of intravitreal dexamethasone on macular edema in von Hippel-Lindau disease assessed using swept-source optical coherence tomography: a case report
- PMID: 30185211
- PMCID: PMC6125864
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-018-1787-8
Effect of intravitreal dexamethasone on macular edema in von Hippel-Lindau disease assessed using swept-source optical coherence tomography: a case report
Abstract
Background: Von Hippel-Lindau disease is a rare hereditary syndrome caused by germinal mutations in a von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressing gene. Retinal hemangioblastoma is the ocular hallmark lesion of von Hippel-Lindau disease.
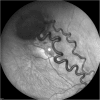
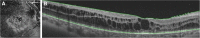
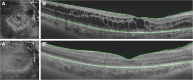
Case presentation: A 20-year-old Caucasian woman presented to our institution with painless visual impairment in the right eye. A fundus ophthalmoscopic evaluation and swept-source optical coherence tomographic examination revealed a retinal hemangioblastoma associated with cystoid macular edema. On the basis of the clinical ocular findings and genetic analysis, von Hippel-Lindau disease was diagnosed. Following an intravitreal injection of ranibizumab, off-label administration of intravitreal dexamethasone was considered to reduce the edema. An almost complete resolution of the edema in the macular area was observed 1 week after the injection. Finally, laser photocoagulation and transconjunctival cryotherapy were performed; the patient developed "ablatio fugax" after cryotherapy.
Conclusions: In our experience, intravitreal dexamethasone administration has proven to be a useful tool for reducing retinal hemangioblastoma-related macular edema in von Hippel-Lindau disease and may be considered a potentially valuable treatment that can be used in combination with other therapies.
Keywords: En face OCT; Innovative biotechnology; Macular edema; Retinal hemangioblastoma; Swept-source OCT; Von Hippel-Lindau disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent for examinations and off-label treatments was obtained from the patient.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined therapy guided by multimodal imaging of fifteen retinal capillary hemangioblastomas in a monocular Von Hippel- Lindau syndrome case report.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 May 6;22(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02409-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35524216 Free PMC article.
-
CLINICALLY INVISIBLE RETINAL HEMANGIOBLASTOMAS DETECTED BY SPECTRAL DOMAIN OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY AND FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY IN TWINS.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2018 Winter;12(1):12-16. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000382. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2018. PMID: 27533642
-
[Von Hippel-Lindau disease : OCTA findings in retinal hemangioma].Ophthalmologe. 2017 Jul;114(7):650-652. doi: 10.1007/s00347-016-0347-0. Ophthalmologe. 2017. PMID: 27671999 German.
-
SPONTANEOUS RESOLUTION OF MACULAR EPIRETINAL MEMBRANES AFTER FLUORESCEIN POTENTIATED ARGON LASER TREATMENT OF VON HIPPEL-LINDAU ASSOCIATED RETINAL HEMANGIOMAS: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2016 Spring;10(2):145-50. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000206. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2016. PMID: 26421964 Review.
-
Stereotactic irradiation for optic nerve hemangioblastoma associated with Von Hippel-Lindau disease: a case report and literature review.Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2023;87(5):78-84. doi: 10.17116/neiro20238705178. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2023. PMID: 37830472 Review. English, Russian.
Cited by
-
Detection of retinal microvascular changes in von Hippel-Lindau disease using optical coherence tomography angiography.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 20;15(2):e0229213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229213. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32078656 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography in pediatric patients: a clinical review.Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb 5;12:2515841420904612. doi: 10.1177/2515841420904612. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32076655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Niemela M, Lemeta S, Sainio M, Rauma S, Pukkala E, Kere J, et al. Hemangioblastomas of the retina: impact of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:1909–1915. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt D, Natt E, Neumann HP. Long-term results of laser treatment for retinal angiomatosis in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Eur J Med Res. 2000;5:47–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

