Outcomes of rituximab therapy in refractory lupus: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30185361
- PMCID: PMC6072690
- DOI: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2018.17096
Outcomes of rituximab therapy in refractory lupus: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Conventional treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN) is associated with damage accrual, hence increased morbidity rate. Off-label use of rituximab (RTX) has shown significant promise in this patient group; however, data are still controversial. We aimed to analyze the outcomes of RTX therapy in refractory lupus using a meta-analysis approach.
Methods: Electronic search of the medical literature was conducted using a combination of relevant keywords to retrieve studies on the safety and efficacy of RTX in SLE and LN patients. Results were screened against our inclusion and exclusion criteria and two reviewers independently extracted the data for analysis. Comprehensive meta-analysis software was used to pool the data from individual studies and provide summary effect estimates.
Results: Thirty-one studies that enrolled 1112 patients were finally eligible for the meta-analysis. The overall global, complete, and partial response rates to RTX therapy were 72%, 46%, and 32%, respectively. RTX significantly decreased Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) and British Isles Lupus Activity Group (BILAG) scores (p<0.001). Prednisone dose was significantly reduced after RTX treatment in both SLE and LN groups (p<0.001), and proteinuria was lowered in SLE (p<0.001) than in LN patients (p=0.07). Infection and infusion-related reactions were the most common side effects.
Conclusion: RTX therapy in refractory SLE and LN patients proved clinical efficacy and favorable safety outcomes. Larger well-designed randomized clinical trials are warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






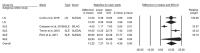

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
