RSPH6A is required for sperm flagellum formation and male fertility in mice
- PMID: 30185526
- PMCID: PMC6198453
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.221648
RSPH6A is required for sperm flagellum formation and male fertility in mice
Abstract
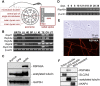
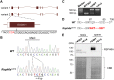
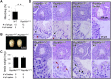
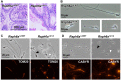
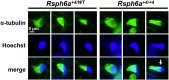
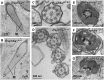
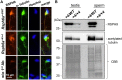
The flagellum is an evolutionarily conserved appendage used for sensing and locomotion. Its backbone is the axoneme and a component of the axoneme is the radial spoke (RS), a protein complex implicated in flagellar motility regulation. Numerous diseases occur if the axoneme is improperly formed, such as primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) and infertility. Radial spoke head 6 homolog A (RSPH6A) is an ortholog of Chlamydomonas RSP6 in the RS head and is evolutionarily conserved. While some RS head proteins have been linked to PCD, little is known about RSPH6A. Here, we show that mouse RSPH6A is testis-enriched and localized in the flagellum. Rsph6a knockout (KO) male mice are infertile as a result of their short immotile spermatozoa. Observation of the KO testis indicates that the axoneme can elongate but is disrupted before accessory structures are formed. Manchette removal is also impaired in the KO testis. Further, RSPH9, another radial spoke protein, disappeared in the Rsph6a KO flagella. These data indicate that RSPH6A is essential for sperm flagellar assembly and male fertility in mice.This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
Keywords: Axoneme; CRISPR/Cas9; Flagella; Radial spoke protein; Spermatozoa.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

