PJA1 Coordinates with the SMC5/6 Complex To Restrict DNA Viruses and Episomal Genes in an Interferon-Independent Manner
- PMID: 30185588
- PMCID: PMC6206484
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00825-18
PJA1 Coordinates with the SMC5/6 Complex To Restrict DNA Viruses and Episomal Genes in an Interferon-Independent Manner
Abstract
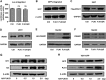
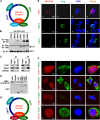
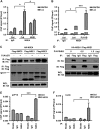
Viral and episomal DNAs, as signs of infections and dangers, induce a series of immune responses in the host, and cells must sense foreign DNAs to eliminate the invaders. The cell nucleus is not "immune privileged" and exerts intrinsic mechanisms to control nuclear-replicating DNA viruses. Thus, it is important to understand the action of viral DNA sensing in the cell nucleus. Here, we reveal a mechanism of restriction of DNA viruses and episomal plasmids mediated by PJA1, a RING-H2 E3 ubiquitin ligase. PJA1 restricts the DNA viruses hepatitis B virus (HBV) and herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) but not the RNA viruses enterovirus 71 (EV71) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). Similarly, PJA1 inhibits episomal plasmids but not chromosome-integrated reporters or endogenous genes. In addition, PJA1 has no effect on endogenous type I and II interferons (IFNs) and interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), suggesting that PJA1 silences DNA viruses independent of the IFN pathways. Interestingly, PJA1 interacts with the SMC5/6 complex (a complex essential for chromosome maintenance and HBV restriction) to facilitate the binding of the complex to viral and episomal DNAs in the cell nucleus. Moreover, treatment with inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases (Tops) and knockdown of Tops release PJA1-mediated silencing of viral and extrachromosomal DNAs. Taken together, results of this work demonstrate that PJA1 interacts with SMC5/6 and facilitates the complex to bind and eliminate viral and episomal DNAs through DNA Tops and thus reveal a distinct mechanism underlying restriction of DNA viruses and foreign genes in the cell nucleus.IMPORTANCE DNA viruses, including hepatitis B virus and herpes simplex virus, induce a series of immune responses in the host and lead to human public health concerns worldwide. In addition to cytokines in the cytoplasm, restriction of viral DNA in the nucleus is an important approach of host immunity. However, the mechanism of foreign DNA recognition and restriction in the cell nucleus is largely unknown. This work demonstrates that an important cellular factor (PJA1) suppresses DNA viruses and transfected plasmids independent of type I and II interferon (IFN) pathways. Instead, PJA1 interacts with the chromosome maintenance complex (SMC5/6), facilitates the complex to recognize and bind viral and episomal DNAs, and recruits DNA topoisomerases to restrict the foreign molecules. These results reveal a distinct mechanism underlying the silencing of viral and episomal invaders in the cell nuclei and suggest that PJA1 acts as a potential agent to prevent infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: DNA topoisomerases; HBV; HSV-1; RING finger protein PJA1; SMC5/6 complex; episomal DNA; extrachromosomal DNA; hepatitis B virus; herpes simplex virus 1; host immune response.
Copyright © 2018 Xu et al.
Figures




References
-
- Roizman B, Knipe DM, Whitley RJ. 2013. Herpes simplex viruses, p 1823–1897. In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Cohen JI, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Racaniello VR, Roizman B (ed), Fields virology, 6th ed Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Schacker T. 2001. The role of HSV in the transmission and progression of HIV. Herpes 8:46–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

