Genome wide association study identifies novel potential candidate genes for bovine milk cholesterol content
- PMID: 30185830
- PMCID: PMC6125589
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31427-0
Genome wide association study identifies novel potential candidate genes for bovine milk cholesterol content
Abstract
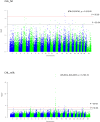
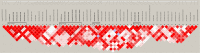
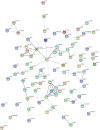
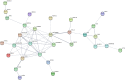
This study aimed to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with milk cholesterol (CHL) content via a genome wide association study (GWAS). Milk CHL content was determined by gas chromatography and expressed as mg of CHL in 100 g of fat (CHL_fat) or in 100 mg of milk (CHL_milk). GWAS was performed with 1,183 cows and 40,196 SNPs using a univariate linear mixed model. Two and 20 SNPs were significantly associated with CHL_fat and CHL_milk, respectively. The important regions for CHL_fat and CHL_milk were at 41.9 Mb on chromosome (BTA) 17 and 1.6-3.2 Mb on BTA 14, respectively. DGAT1, PTPN1, INSIG1, HEXIM1, SDS, and HTR5A genes, also known to be associated with human plasma CHL phenotypes, were identified as potential candidate genes for bovine milk CHL. Additional new potential candidate genes for milk CHL were RXFP1, FAM198B, TMEM144, CXXC4, MAML2 and CDH13. Enrichment analyses suggested that identified candidate genes participated in cell-cell signaling processes and are key members in tight junction, focal adhesion, Notch signaling and glycerolipid metabolism pathways. Furthermore, identified transcription factors such as PPARD, LXR, and NOTCH1 might be important in the regulation of bovine milk CHL content. The expression of several positional candidate genes (such as DGAT1, INSIG1 and FAM198B) and their correlation with milk CHL content were further confirmed with RNA sequence data from mammary gland tissues. This is the first GWAS on bovine milk CHL. The identified markers and candidate genes need further validation in a larger cohort for use in the selection of cows with desired milk CHL content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted genotyping to identify potential functional variants associated with cholesterol content in bovine milk.Anim Genet. 2020 Mar;51(2):200-209. doi: 10.1111/age.12901. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Anim Genet. 2020. PMID: 31913546
-
Genome-wide association study of milk fatty acid composition in Italian Simmental and Italian Holstein cows using single nucleotide polymorphism arrays.J Dairy Sci. 2018 Dec;101(12):11004-11019. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14413. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Dairy Sci. 2018. PMID: 30243637
-
Genome-wide association analysis and pathways enrichment for lactation persistency in Canadian Holstein cattle.J Dairy Sci. 2017 Mar;100(3):1955-1970. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11910. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Dairy Sci. 2017. PMID: 28088409
-
Multi-population GWAS and enrichment analyses reveal novel genomic regions and promising candidate genes underlying bovine milk fatty acid composition.BMC Genomics. 2019 Mar 6;20(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5573-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30841852 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression in dairy cows under negative energy balance and ketosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Dairy Sci. 2021 Jan;104(1):602-615. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18883. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 33189279
Cited by
-
Advances in fatty acids nutrition in dairy cows: from gut to cells and effects on performance.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020 Nov 16;11(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00512-8. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33292523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Population Structure and Selective Signatures for Milk Production Traits in Xinjiang Brown Cattle and Chinese Simmental Cattle.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 25;26(5):2003. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052003. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076627 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Parameter Estimation and Genome-Wide Association Study-Based Loci Identification of Milk-Related Traits in Chinese Holstein.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 28;12:799664. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.799664. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35154251 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Cell Atlas of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Reveals Mechanisms That Regulate Intramuscular Adipogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 1;25(23):12935. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312935. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684644 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Genetic Markers for Milk Yield in Xinjiang Donkeys: A Genome-Wide Association Study and Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR-Based Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 25;26(7):2961. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072961. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Do, D. N. et al. Genetic parameters of milk cholesterol content in Holstein cattle. Canadian J. Anim. Sci., 10.1139/CJAS-2018-0010 (Published on the web on 27 April 2018) (2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

