Exercise, energy balance and body composition
- PMID: 30185845
- PMCID: PMC6125254
- DOI: 10.1038/s41430-018-0180-4
Exercise, energy balance and body composition
Abstract
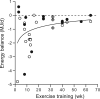
Activity-induced energy expenditure, as determined by the activity pattern including exercise, is the most variable component of daily energy expenditure. Here, the focus is on effects of exercise training on energy balance and body composition in subjects with a sedentary or light-active lifestyle. Then, exercise training induces an energy imbalance consistently lower than prescribed energy expenditure from exercise. Additionally, individual responses are highly variable and decrease in time. Combining the results from 23 exercise training studies in normal-weight, overweight, and obese subjects, varying in duration from 2 to 64 weeks, showed an average initial energy imbalance of about 2 MJ/day with an exponential decline to nearly zero after about 1 year. A compensatory increase in energy intake is the most likely explanation for the lower than expected effect of exercise on energy balance. Overall, exercise training results in a healthier body composition as reflected by a reduction of body fat, especially in overweight and obese subjects, with little or no long-term effect on body weight.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Exercise Training on Total Daily Energy Expenditure and Body Composition in Weight-Stable Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Trial.J Phys Act Health. 2020 Apr 1;17(4):456-463. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2019-0415. J Phys Act Health. 2020. PMID: 32176862 Clinical Trial.
-
Regulation of energy balance during long-term physical inactivity induced by bed rest with and without exercise training.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Mar;95(3):1045-53. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1005. Epub 2010 Jan 8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20061436 Clinical Trial.
-
Spontaneous activity responses to exercise in males and females.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006 Sep;60(9):1055-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602417. Epub 2006 Feb 22. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16493451 Clinical Trial.
-
Energy metabolism and obesity.Med Clin North Am. 2000 Mar;84(2):347-62. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70225-x. Med Clin North Am. 2000. PMID: 10793646 Review.
-
Contributing factors and variability of energy expenditure in non-obese, obese, and post-obese adolescents.Reprod Nutr Dev. 2005 Mar-Apr;45(2):129-42. doi: 10.1051/rnd:2005014. Reprod Nutr Dev. 2005. PMID: 15952420 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Fatigue Effects of Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide and Effervescent Tablets by Regulating Oxidative Stress and Energy Metabolism in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 18;23(18):10920. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810920. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142831 Free PMC article.
-
Body Composition in Chronic Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):964. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020964. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in the Level of Asprosin as a Novel Adipocytokine after Different Types of Resistance Training.J Chem Health Risks. 2021 Summer;11(Spec Issue):179-188. J Chem Health Risks. 2021. PMID: 35106290 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Diet, Physical Activity and Nutritional Status of Male Border Guard Officers.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 27;19(9):5305. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095305. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564700 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of the Pro12Ala Polymorphism on the PPARy2 Gene With the Body Composition of Practitioners of Cyclic Exercises.Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 12;11:633721. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.633721. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33510651 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

