In vivo reprogramming of wound-resident cells generates skin epithelial tissue
- PMID: 30185909
- PMCID: PMC9651909
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0477-4
In vivo reprogramming of wound-resident cells generates skin epithelial tissue
Abstract
Large cutaneous ulcers are, in severe cases, life threatening1,2. As the global population ages, non-healing ulcers are becoming increasingly common1,2. Treatment currently requires the transplantation of pre-existing epithelial components, such as skin grafts, or therapy using cultured cells2. Here we develop alternative supplies of epidermal coverage for the treatment of these kinds of wounds. We generated expandable epithelial tissues using in vivo reprogramming of wound-resident mesenchymal cells. Transduction of four transcription factors that specify the skin-cell lineage enabled efficient and rapid de novo epithelialization from the surface of cutaneous ulcers in mice. Our findings may provide a new therapeutic avenue for treating skin wounds and could be extended to other disease situations in which tissue homeostasis and repair are impaired.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
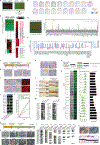

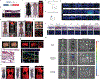



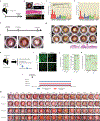
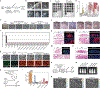





Comment in
-
Wound, heal thyself.Nat Med. 2018 Sep;24(9):1311-1312. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0179-3. Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 30194410 No abstract available.
-
More than One Way to Skin a Wound.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Nov 1;23(5):636-638. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.014. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30388420
References
-
- Sun BK, Siprashvili Z & Khavari PA Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds. Science 346, 941–945 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y & Longaker MT Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 453, 314–321 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K & Yamanaka S Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

