Population dynamics of normal human blood inferred from somatic mutations
- PMID: 30185910
- PMCID: PMC6163040
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0497-0
Population dynamics of normal human blood inferred from somatic mutations
Abstract
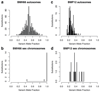
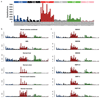
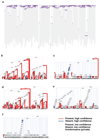
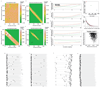
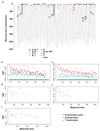
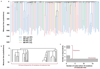
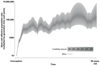
Haematopoietic stem cells drive blood production, but their population size and lifetime dynamics have not been quantified directly in humans. Here we identified 129,582 spontaneous, genome-wide somatic mutations in 140 single-cell-derived haematopoietic stem and progenitor colonies from a healthy 59-year-old man and applied population-genetics approaches to reconstruct clonal dynamics. Cell divisions from early embryogenesis were evident in the phylogenetic tree; all blood cells were derived from a common ancestor that preceded gastrulation. The size of the stem cell population grew steadily in early life, reaching a stable plateau by adolescence. We estimate the numbers of haematopoietic stem cells that are actively making white blood cells at any one time to be in the range of 50,000-200,000. We observed adult haematopoietic stem cell clones that generate multilineage outputs, including granulocytes and B lymphocytes. Harnessing naturally occurring mutations to report the clonal architecture of an organ enables the high-resolution reconstruction of somatic cell dynamics in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




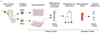

References
-
- Till JE, McCulloch EA. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961;14:213–22. - PubMed
-
- Becker AJ, McCulloch EA, Till JE. Cytological demonstration of the clonal nature of spleen colonies derived from transplanted mouse marrow cells. Nature. 1963;197:452–4. - PubMed
-
- Lemischka IR, Raulet DH, Mulligan RC. Developmental potential and dynamic behavior of hematopoietic stem cells. Cell. 1986;45:917–27. - PubMed
-
- Naik SH, et al. Diverse and heritable lineage imprinting of early haematopoietic progenitors. Nature. 2013;496:229–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

