M-Calpain Activation Facilitates Seizure Induced KCC2 Down Regulation
- PMID: 30186110
- PMCID: PMC6110871
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00287
M-Calpain Activation Facilitates Seizure Induced KCC2 Down Regulation
Abstract
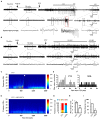
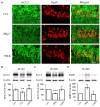
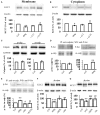
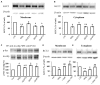
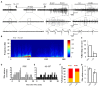
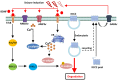
Potassium chloride co-transporter 2 (KCC2), a major chloride transporter that maintains GABAA receptor inhibition in mature mammalian neurons, is down-regulated in the hippocampus during epileptogenesis. Impaired KCC2 function accelerates or facilitates seizure onset. Calpain, with two main subtypes of m- and μ-calpain, is a Ca2+-dependent cysteine protease that mediates the nonlysosomal degradation of KCC2. Although recent studies have demonstrated that calpain inhibitors exert antiepileptic and neuroprotective effects in animal models of acute and chronic epilepsy, whether calpain activation affects seizure induction through KCC2 degradation remains unknown. Our results showed that: (1) Blockade of calpain by non-selective calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 prevented convulsant stimulation induced KCC2 downregulation, and reduced the incidence and the severity of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) induced seizures. (2) m-calpain, but not μ-calpain, inhibitor mimicked MDL-28170 effect on preventing KCC2 downregulation. (3) Phosphorylation of m-calpain has been significantly enhanced during seizure onset, which was partly mediated by the calcium independent MAPK/ERK signaling pathway activation. (4) MAPK/ERK signaling blockade also had similar effect as total calpain blockade on both KCC2 downregulation and animal seizure induction. The results indicate that upregulated m-calpain activation by MAPK/ERK during convulsant stimulation down regulates both cytoplasm- and membrane KCC2, and in turn facilitates seizure induction. This finding may provide a foundation for the development of highly effective antiepileptic drugs targeting of m-calpain.
Keywords: KCC2; MAPK/ERK; PTZ; calpain; epilepsy.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

