Antidepressant-Like Effects of Cistanche tubulosa Extract on Chronic Unpredictable Stress Rats Through Restoration of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis
- PMID: 30186183
- PMCID: PMC6112285
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00967
Antidepressant-Like Effects of Cistanche tubulosa Extract on Chronic Unpredictable Stress Rats Through Restoration of Gut Microbiota Homeostasis
Abstract
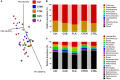
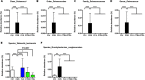
Growing evidence shows that neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, are linked with gut microbiome through the gut-brain axis. Cistanches Herba is well known for the treatment of "kidney-yang" deficiency in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and has been used for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in recent years. In this study, chronic unpredictable stress (CUS)-induced depression model was established to explore the impact of Cistanche tubulosa extract (CTE) on behavioral tests, monoamine neurotransmitters and neurotrophic factors in hippocampus and colon, gut microbiota composition, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) production. Moreover, correlation analysis was used to evaluate the functional relationship between altered gut microbiota, changed neurotransmitters and neurotrophins in hippocampus and colon, and disturbed concentration of SCFAs. CTE significantly improved depression-like behaviors in rats under CUS. Brain level of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in CUS rats were restored by CTE. The relative abundance of gut microbiota and the concentrations of acetate and hexanoic acid could also be modulated by CTE treatment. We further showed that the application of CTE in CUS rats led to strong correlation among disrupted gut microbiota composition, hippocampus neurotransmitter levels, and production of neuroactive metabolite SCFAs. Altogether, these results identify CTE as a potential treatment for depressive symptoms by restoring homeostasis of gut microbiota for microbiota-gut-brain axis disorders, opening new avenues in the field of neuropsychopharmacology.
Keywords: Cistanche tubulosa; antidepressant; chronic unpredictable stress; gut microbiota; microbiota–gut–brain axis.
Figures
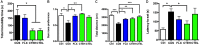
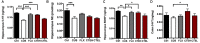


Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo metabolism of Cistanche tubulosa extract in normal and chronic unpredictable stress-induced depressive rats.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;1125:121728. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121728. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31352203
-
Total glycosides from stems of Cistanche tubulosa alleviate depression-like behaviors: bidirectional interaction of the phytochemicals and gut microbiota.Phytomedicine. 2021 Mar;83:153471. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153471. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33636477
-
Gut microbiota-SCFAs-brain axis associated with the antidepressant activity of berberine in CUMS rats.J Affect Disord. 2023 Mar 15;325:141-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.12.166. Epub 2023 Jan 5. J Affect Disord. 2023. PMID: 36610597
-
Crosstalk between the microbiota-gut-brain axis and depression.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 3;6(6):e04097. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04097. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32529075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Depression: Emerging Therapeutic Avenues.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023;22(2):276-288. doi: 10.2174/1871527321666220329140804. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 35352640 Review.
Cited by
-
Highly Efficient Adsorption of Phenylethanoid Glycosides on Mesoporous Carbon.Front Chem. 2019 Nov 14;7:781. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00781. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31799240 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prolonged escitalopram administration on long-term potentiation within the hippocampal CA1 area in rats under predictable and unpredictable chronic mild stress.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Dec;39(8):1481-1494. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01399-4. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39240474
-
Effects of the Cistanche tubulosa Aqueous Extract on the Gut Microbiota of Mice with Intestinal Disorders.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jul 14;2021:4936970. doi: 10.1155/2021/4936970. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34335809 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the active components of Baihe-Zhimu decoction that ameliorate depressive disease by an effective integrated strategy: a systemic pharmacokinetics study combined with classical depression model tests.Chin Med. 2019 Sep 24;14:37. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0254-9. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31572489 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional processing increases biological activities of Dendrobium offificinale Kimura et. Migo in Southeast Yunnan, China.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 31;12(1):14814. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17628-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36045147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bravo J. A., Forsythe P., Chew M. V., Escaravage E., Savignac H. M., Dinan T. G., et al. (2011). Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 16050–16055. 10.1073/pnas.1102999108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burokas A., Arboleya S., Moloney R. D., Peterson V. L., Murphy K., Clarke G., et al. (2017). Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 82 472–487. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.12.031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cai L., Li R., Tang W. J., Meng G., Hu X. Y., Wu T. N. (2015). Antidepressant-like effect of geniposide on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive rats by regulating the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmcol. 25 1332–1341. 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.04.009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

