Non-viral Delivery of Nucleic Acids: Insight Into Mechanisms of Overcoming Intracellular Barriers
- PMID: 30186185
- PMCID: PMC6111240
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00971
Non-viral Delivery of Nucleic Acids: Insight Into Mechanisms of Overcoming Intracellular Barriers
Abstract
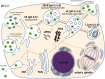
Delivery of genes, including plasmid DNAs, short interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and messenger RNAs (mRNAs), using artificial non-viral nanotherapeutics is a promising approach in cancer gene therapy. However, multiple physiological barriers upon systemic administration remain a key challenge in clinical translation of anti-cancer gene therapeutics. Besides extracellular barriers including sequestration of gene delivery nanoparticles from the bloodstream by resident organ-specific macrophages, and their poor extravasation and tissue penetration in tumors, overcoming intracellular barriers is also necessary for successful delivery of nucleic acids. Whereas for RNA delivery the endosomal barrier holds a key importance, transfer of DNA cargo additionally requires translocation into the nucleus. Better understanding of crossing membrane barriers by nucleic acid nanoformulations is essential to the improvement of current non-viral carriers. This review aims to summarize relevant literature on intracellular trafficking of non-viral nanoparticles and determine key factors toward surmounting intracellular barriers. Moreover, recent data allowed us to propose new interpretations of current hypotheses of endosomal escape mechanisms of nucleic acid nanoformulations.
Keywords: endosomal escape; gene delivery; intracellular trafficking; lipoplexes; polyplexes; siRNA delivery.
Figures
References
-
- Becker M. L., Fagan J. A., Gallant N. D., Bauer B. J., Bajpai V., Hobbie E. K., et al. (2007). Length-dependent uptake of DNA-wrapped single-walled carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 19 939–945. 10.1002/adma.200602667 - DOI
-
- Bishop C. J., Majewski R. L., Guiriba T.-R. M., Wilson D. R., Bhise N. S., Quiñones-Hinojosa A., et al. (2016). Quantification of cellular and nuclear uptake rates of polymeric gene delivery nanoparticles and DNA plasmids via flow cytometry. Acta Biomater. 37 120–130. 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

