The Potential Role of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4-Like Activity From the Gut Microbiota on the Host Health
- PMID: 30186247
- PMCID: PMC6113382
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01900
The Potential Role of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4-Like Activity From the Gut Microbiota on the Host Health
Abstract
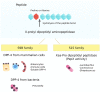
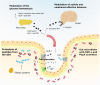
The Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) activity influences metabolic, behavioral and intestinal disorders through the cleavage of key hormones and peptides. Some studies describe the existence of human DPP-4 homologs in commensal bacteria, for instance in Prevotella or Lactobacillus. However, the role of the gut microbiota as a source of DPP-4-like activity has never been investigated. Through the comparison of the DPP-4 activity in the cecal content of germ-free mice (GFM) and gnotobiotic mice colonized with the gut microbiota of a healthy subject, we bring the proof of concept that a significant DPP-4-like activity occurs in the microbiota. By analyzing the existing literature, we propose that DPP-4-like activity encoded by the intestinal microbiome could constitute a novel mechanism to modulate protein digestion as well as host metabolism and behavior.
Keywords: DPP-4 activity; PepX activity; behavior; gut microbiota; metabolism; microbiome.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commentary: The Potential Role of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4-Like Activity From the Gut Microbiota on the Host Health.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 10;9:3313. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03313. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30687289 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmed R. H., Huri H. Z., Muniandy S., Al-Hamodi Z., Al-Absi B., Alsalahi A., et al. (2017). Altered circulating concentrations of active glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) in obese subjects and their association with insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. 50, 746–749. 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anastasiou R., Papadelli M., Georgalaki M. D., Kalantzopoulos G., Tsakalidou E. (2002). Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding X-prolyl-dipeptidyl aminopeptidase (PepX) from Streptococcus thermophilus strain ACA-DC 4. J. Appl. Microbiol. 93, 52–59. 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2002.01659.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

