Assessment of Molecular Measures in Non-FXTAS Male Premutation Carriers
- PMID: 30186307
- PMCID: PMC6113865
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00302
Assessment of Molecular Measures in Non-FXTAS Male Premutation Carriers
Abstract
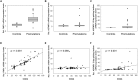
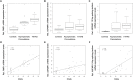
Approximately 30-40% of male and 8-16% of female carriers of the Fragile X premutation will develop a neurodegenerative movement disorder characterized by intentional tremor, gait ataxia, autonomic dysfunction, cognitive decline, and Parkinsonism during their lifetime. At the molecular level, premutation carriers have increased expression levels of the FMR1 and the antisense FMR1 (ASFMR1) mRNAs. Both genes undergo alternative splicing giving rise to a number of different transcripts. Alteration in the alternative splicing process might be associated with FXTAS. In this study, we have investigated the correlation between objective measures of movement (balance and tremor using the CATSYS battery) and the expression of both the FMR1 and the ASFMR1 genes. In addition, we investigated whether their expression level and that of the ASFMR1 131 bp splice isoform could distinguish between premutation carriers with FXTAS and non-FXTAS premutation carriers. Confirming previous findings, the expression levels of transcripts at the FMR1 locus positively correlated with the CGG repeat number and significantly differentiated the premutation carriers from the control groups. Furthermore, premutation carriers with and without FXTAS, showed a significant difference in the expression level of the ASFMR1 131 bp splice isoform when compared to age and gender matched controls. However, there was no significant difference in the ASFMR1 131 bp splice isoform expression level when comparing premutation carriers with and without FXTAS. Finally, our results indicate significant group differences in CATSYS dominant hand reaction time and postural sway with eyes closed in premutation carriers without FXTAS compared to controls. In addition, a significant inverse association between the tremor intensity and the expression level of ASFMR1 131 bp splice isoform in premutation carriers compared to controls, was observed, suggesting a potential role in the pathogenesis of FXTAS.
Keywords: ASFMR1; CATSYS; FMR1; FXTAS; premutation; splicing isoforms; transcription.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and Alternative Splicing of the Antisense FMR1 (ASFMR1) Gene.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;60(4):2051-2061. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03176-9. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36598648 Free PMC article.
-
Static and dynamic postural control deficits in aging fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene premutation carriers.J Neurodev Disord. 2019 Jan 21;11(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s11689-018-9261-x. J Neurodev Disord. 2019. PMID: 30665341 Free PMC article.
-
ASFMR1 splice variant: A predictor of fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome.Neurol Genet. 2018 Jul 27;4(4):e246. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000246. eCollection 2018 Aug. Neurol Genet. 2018. PMID: 30065951 Free PMC article.
-
Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Development of Therapeutics.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 May 5;11:128. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00128. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28529475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[FMR1 PREMUTATION CARRIERS - ARE THEY REALLY ASYMPTOMATIC?].Harefuah. 2018 Apr;157(4):241-244. Harefuah. 2018. PMID: 29688643 Review. Hebrew.
Cited by
-
FMR1 locus isoforms: potential biomarker candidates in fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS).Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 6;10(1):11099. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67946-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32632326 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Large Deletion Leading to Fragile X Syndrome.Front Genet. 2022 May 11;13:884424. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.884424. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35646065 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Alternative Splicing of the Antisense FMR1 (ASFMR1) Gene.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Apr;60(4):2051-2061. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03176-9. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36598648 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis and Peripheral Monitoring of Adult Fragile X-Associated Syndromes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 4;22(16):8368. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168368. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Després C., Lamoureux D., Beuter A. (2000). Standardization of a neuromotor test battery: the CATSYS system. Neurotoxicology 21 725–735. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

