Effect of He's Santong Needling Method on Dysphagia after Stroke: A Study Protocol for a Prospective Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial
- PMID: 30186356
- PMCID: PMC6112255
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6126410
Effect of He's Santong Needling Method on Dysphagia after Stroke: A Study Protocol for a Prospective Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial
Abstract
Background: Dysphagia is a common complication of stroke, affecting up to 78% of stroke patients. The existence of dysphagia after stroke has been associated with an increased risk for pulmonary complications and even mortality. Previous studies have shown that acupuncture could be potential therapeutic method for treatment of dysphagia after stroke. A prospective randomized controlled pilot trial is designed to evaluate the effect of He's Santong needling method on dysphagia after stroke.
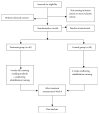
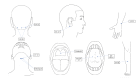
Methods and design: Sixty eligible participants will be recruited and randomly assigned into treatment group (He's Santong needling method and swallowing rehabilitation training) and control group (swallowing rehabilitation training) in a 1:1 ratio. All treatments will be provided everyday on weekdays with a two-day interval at the weekend, during a total treatment course of four weeks. The Penetration-Aspiration Scale with Fiberoptic Endoscopic Examination of Swallowing will be assessed at baseline and endpoint (Week 4) as primary outcomes. The Saitoh's classification score, Swallowing-Related Quality of Life score, the Modified Mann Assessment of Swallowing Ability score, and Surface Electromyography will be evaluated at baseline and endpoint as secondary outcomes.
Ethics and dissemination: The trial protocol has been approved by the Research Ethical Committee of Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Capital Medical University on 9 May 2017 (ethical batch number: 2017BL-013-02). Each participant will be notified regarding the study protocol. Written informed consent will be obtained from each participant.
Trial registration: ISRCTN registry: ISRCTN68981054; Registered on 25 September 2017.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Observation on the efficacy of post-stroke dysphagia treated with He's santong acupuncture therapy through surface electromyography: a randomized controlled trial].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Mar 25;47(3):256-61. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210197. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35319844 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[He's Santong needling method for neurological functional deficit in the patient of ischemic apoplexy: randomized controlled multi-central study].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006 May;26(5):309-12. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006. PMID: 16739838 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of video-game based swallowing function training in patients with dysphagia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2023 Nov 16;24(1):735. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07738-7. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37974234 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for Poststroke Dysphagia: A Pilot, Nonrandomized, Self-Controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 May 11;2020:4689296. doi: 10.1155/2020/4689296. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32454860 Free PMC article.
-
[Observation on therapeutic effect of He's Santong needling methods on cold erythema multiforme].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2009 Oct;29(10):807-9. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2009. PMID: 19873917 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources