MicroRNA-126 accelerates IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation associated with the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by promoting Ca2+ influx
- PMID: 30186504
- PMCID: PMC6122504
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6510
MicroRNA-126 accelerates IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation associated with the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by promoting Ca2+ influx
Abstract
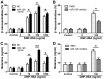
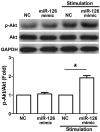
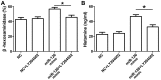
Mast cells (MCs) have been reported to serve a crucial role in allergic diseases, including asthma, allergic rhinitis and anaphylaxis. A previous study revealed that microRNA-126 (miR-126) was associated with airway hyperresponsiveness induced by house dust mites, however the molecular mechanisms were unclear. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of miR-126 on immunoglobulin E (IgE)-regulated MC degranulation and explore its underlying mechanisms. miR-126 expression was quantified using a rat model in vivo and in rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMCs) in vitro. Overexpression or downregulation of miR-126 was established by transfection with miR-126 mimics or miR-126 inhibitors and MC degranulation was subsequently evaluated. The effect of miR-126 on protein kinase B (Akt) and phosphorylated Akt protein expression was examined by western blot analysis. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor (LY294002) was used to determine the role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. In addition, cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) levels were measured by a fura-2 assay. The results demonstrated that miR-126 expression was upregulated in the ear tissues of rats with allergic contact dermatitis and IgE-activated MCs. The overexpression of miR-126 in RPMCs was established following miR-126 mimic transfection. The release of β-hexosaminidase and histamine, markers of MC degranulation, were significantly increased in cells with miR-126 overexpression. The phosphorylation of Akt was significantly increased following transfection with miR-126 mimics in stimulated cells, however the signaling activation was abrogated by LY294002. In addition, Ca2+ influx was significantly promoted in stimulated RPMCs overexpressing miR-126. These results indicate that miR-126 accelerated IgE-mediated MC degranulation associated with the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by promoting Ca2+ influx. This suggests that miR-126 may be a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of allergic skin diseases.
Keywords: Ca2+ influx; allergic skin diseases; mast cells; microRNA-126; phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Propofol attenuates mast cell degranulation via inhibiting the miR-221/PI3K/Akt/Ca2+ pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Aug;16(2):1426-1432. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6317. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30116391 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-221 promotes IgE-mediated activation of mast cells degranulation by PI3K/Akt/PLCγ/Ca(2+) pathway.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016 Jun;48(3):293-9. doi: 10.1007/s10863-016-9659-7. Epub 2016 Apr 25. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016. PMID: 27113449
-
MicroRNA-21-Mediated Inhibition of Mast Cell Degranulation Involved in the Protective Effect of Berberine on 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Allergic Contact Dermatitis in Rats via p38 Pathway.Inflammation. 2018 Mar;41(2):689-699. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0723-1. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29282578
-
Down-regulation of microRNA-223 promotes degranulation via the PI3K/Akt pathway by targeting IGF-1R in mast cells.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 13;10(4):e0123575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123575. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25875646 Free PMC article.
-
Spike proteins of coronaviruses activate mast cells for degranulation via stimulating Src/PI3K/AKT/Ca2+ intracellular signaling cascade.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0007825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00078-25. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40304504 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Mar 24;8(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01344-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36964157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in mast cell activation and regulation.F1000Res. 2020 Mar 19;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-196. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.22037.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32226609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Role for Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor 1 in Modulating FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation.J Immunol. 2021 Feb 1;206(3):471-480. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000671. Epub 2020 Dec 23. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33361207 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of MicroRNAs in Nasal Inflammatory Diseases and Tumors: From Bench to Bedside.Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 28;16(3):295. doi: 10.3390/genes16030295. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Crosstalk between FcεRI and Sphingosine Signaling in Allergic Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 11;23(22):13892. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213892. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430378 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Le DD, Schmit D, Heck S, Omlor AJ, Sester M, Herr C, Schick B, Daubeuf F, Fähndrich S, Bals R, et al. Increase of mast cell-nerve association and neuropeptide receptor expression on mast cells in perennial allergic rhinitis. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2016;23:261–270. doi: 10.1159/000453068. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
