Wear particles enhance autophagy through up-regulation of CD147 to promote osteoclastogenesis
- PMID: 30186567
- PMCID: PMC6118083
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.29347.7093
Wear particles enhance autophagy through up-regulation of CD147 to promote osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
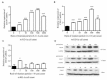
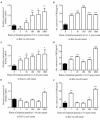
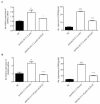
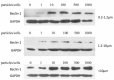
Objectives: The study aimed to uncover the underlying mechanism linking wear particles to osteoclast differentiation, and we explored the effect of titanium particles of different sizes on CD147 expression and autophagy in macrophages.
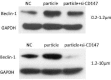
Materials and methods: Effects of titanium particles on CD147 and RANKL mRNA were detected by QPCR; protein level of CD147 and Beclin-1 were detected by Western blot; soluble RANKL were detected by ELISA. To determine the effect of CD147 and autophagy, KG-1a cells were transfected with siRNA-CD147 or treated with autophagy inhibitor CQ (chloroquine), and then co-cultured with different sizes of titanium particles.
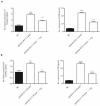
Results: Our results showed that 0.2-1.2 µm and 1.2-10 µm titanium particles up-regulate CD147 to activate autophagy, which increase the level of soluble RANKL to promote osteoclastogenesis. Suppression of CD147 with siRNA could diminish particle-induced autophagy and soluble RANKL expression. In addition, CQ could dramatically reduce particle-induced soluble RANKL expression.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested a possible mechanism underlying wear debris-induced osteolysis and identified CD147 as a potential therapeutic target in aseptic loosening.
Keywords: Autophagy; CD147; Osteoclastogenesis; Peri-implant osteolysis; RANKL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TiAl6V4 particles promote osteoclast formation via autophagy-mediated downregulation of interferon-beta in osteocytes.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 15;48:489-498. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27838463
-
Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate represses osteoclastogenesis and prevents wear debris-induced osteolysis via suppression of ERK pathway.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 15;48:479-488. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.022. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27838465
-
Netrin-1 regulates ERK1/2 signaling pathway and autophagy activation in wear particle-induced osteoclastogenesis.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Mar;45(3):612-622. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11544. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 33386763 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A as a new target for downregulating osteoclastogenesis and alleviating titanium particle-induced bone resorption.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jun;73:488-499. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29656074
-
Adenovirus-mediated small interfering RNA targeting tumor necrosis factor-α inhibits titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption.Int J Mol Med. 2013 Aug;32(2):296-306. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1416. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23760678
Cited by
-
The dual role of autophagy in periprosthetic osteolysis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 24;11:1123753. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1123753. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37035243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Bone Metabolic Disorders.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jul 30;16(14):2675-2691. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.46627. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32792864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine on bone health (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jun;31(6):168. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13533. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40243121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subchondral osteoclasts and osteoarthritis: new insights and potential therapeutic avenues.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Apr 25;56(4):499-512. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024017. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38439665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone regeneration strategies based on organelle homeostasis of mesenchymal stem cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 17;14:1151691. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1151691. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37033227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hallab NJ, Jacobs JJ. Biologic effects of implant debris. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Crotti TN, Smith MD, Findlay DM, Zreiqat H, Ahern MJ, Weedon H, et al. Factors regulating osteoclast formation in human tissues adjacent to peri-implant bone loss: expression of receptor activator NFkappaB, RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin. Biomaterials. 2004;25:565–573. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
