A Comprehensive Look at Irritable Bowel Syndrome and its Associated Factors Considering the Rome IV Criteria: A Penalized Smoothly Clipped Absolute Deviation Regression Approach in the Pars Cohort Study
- PMID: 30186578
- PMCID: PMC6119837
- DOI: 10.15171/mejdd.2018.104
A Comprehensive Look at Irritable Bowel Syndrome and its Associated Factors Considering the Rome IV Criteria: A Penalized Smoothly Clipped Absolute Deviation Regression Approach in the Pars Cohort Study
Abstract
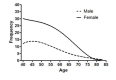
BACKGROUND After the introduction of the Rome IV criteria for the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), studies on the clinical significance of the new criteria in the settings of a large study has been scarce. Objective: Herein we used the infrastructures provided by one the largest cohort studies in Iran to evaluate the epidemiological features related to IBS. METHODS A total of 9264 participants, were enrolled in the initial registry. Diagnosis of IBS was done using the Rome IV criteria. Individuals with IBS were compared with a control group. Since the study included a large sample size of patients, we used the penalized smoothly clipped absolute deviation (SCAD) regression analysis to construct a model for the evaluation of factors associated with IBS. RESULTS Overall, data of 9163 participants entered the final analysis. In total, 1067 (11.6%) individuals were diagnosed with IBS, among which 57 (5.3%) were diarrhea dominant (IBS-D), 380 (35.6%) were constipation dominant (IBS-C), and 630 (59%) did not mention having any of the two (IBS-U). In the regression model, back pain/arthralgia (OR: 1.98, 95% CI: 1.65 - 2.40), insomnia (OR: 1.65, 95% CI: 1.40 - 1.93), depression (OR: 1.64, 95% CI: 1.38 - 1.95), female sex (OR: 1.58, 95% CI: 1.27 - 1.96), anxiety (OR: 1.43, 95% CI: 1.21 - 1.69), and being married (OR: 1.23, 95% CI: 1.03 - 1.48), were associated with higher rates of IBS. We found that IBS prevalence displays a peak at the age of 41 years for both men and women. CONCLUSION The present study provides a background for follow-up studies to be conducted in order to evaluate causality between IBS and some major diseases such as liver disease. We also found that opium use, although not statistically significant, in addition to sex, education, back/joint pain, depression, insomnia, anxiety, and marital status might be a contributing factor in IBS.
Keywords: Opium; Cohort; Iran; Irritable bowel syndrome; Liver disease; Oral health; Risk factor; Rome IV.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this work.
Similar articles
-
Global prevalence and risk factors of irritable bowel syndrome from 2006 to 2024 using the Rome III and IV criteria: a meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Apr 30. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002994. Online ahead of print. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40359286
-
Quantifying Rome symptoms for diagnosis of the irritable bowel syndrome.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018 Sep;30(9):e13356. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13356. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018. PMID: 29701271
-
Subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome on Rome III criteria: a multicenter study.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Apr;27(4):760-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06930.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 21929652
-
Rome Criteria and a Diagnostic Approach to Irritable Bowel Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2017 Oct 26;6(11):99. doi: 10.3390/jcm6110099. J Clin Med. 2017. PMID: 29072609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Transaminitis and Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Cureus. 2021 Jul 23;13(7):e16583. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16583. eCollection 2021 Jul. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34322359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and Correlates of Polypharmacy, and Drug Utilization Pattern in a Semi-urban Population: Results from the Pars Cohort Study.Arch Iran Med. 2023 Mar 1;26(3):156-165. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.24. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 37543938 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in irritable bowel syndrome: More than a coincidence?World J Hepatol. 2021 Dec 27;13(12):1816-1827. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1816. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 35069992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health anxiety in medical employees: A multicentre study.J Int Med Res. 2019 Oct;47(10):4854-4861. doi: 10.1177/0300060519872310. Epub 2019 Sep 6. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31638465 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Changes of the Pituitary Gland in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging.J Imaging. 2024 Sep 13;10(9):226. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10090226. J Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39330446 Free PMC article.
-
Symptom management needs of patients with irritable bowel syndrome and concurrent anxiety and/or depression: A qualitative study.J Adv Nurs. 2023 Feb;79(2):775-788. doi: 10.1111/jan.15532. Epub 2022 Dec 13. J Adv Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36511394 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous