Assessment of Ambient Air Pollution in Istanbul during 2003-2013
- PMID: 30186785
- PMCID: PMC6123589
Assessment of Ambient Air Pollution in Istanbul during 2003-2013
Abstract
Background: We investigated the air quality changes from 2003-2013 in Istanbul, Turkey.
Methods: We studied SO2, CO and PM concentration patterns in 10 districts of Istanbul. The data was obtained from air pollution monitoring stations of Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality Environmental Protection Department. We compared the variations of mean concentrations monthly, yearly and seasonally. The winter season was accepted from Oct to Mar and the summer season from Apr to Sep.
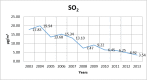
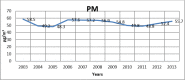
Results: The highest monthly average values for all measurements of sulfur dioxide and CO were 12.61, 949.19 μg/m3 in Sarachane respectively. The Highest value of the monthly average of the Particulate Matter was 72.07 μg/m3 in Kartal district. During the period between 2003-2013, monthly mean concentration values of different districts differed significantly in levels of SO2 (P=0.012), CO (P=0.029), and PM (P=0.024).
Conclusion: The emissions of air pollutants (SO2, PM, and CO) decreased considerably from 2003 to 2013.
Keywords: Air; Health; Particular matter (PM); Pollution.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fenger J. (1999). Urban air quality. Atmos Environ, 33: 4877–4900.
-
- Riga-Karandinos AN, Saitanis C. (2005). Comparative assessment of ambient air quality in two typical Mediterranean coastal cities in Greece. Chemosphere, 59:1125–36. - PubMed
-
- Özden Ö, Döğeroğlu T, Kara S. (2008). Assessment of ambient air quality in Eskişehir, Turkey. Environ Int, 34:678–87. - PubMed
-
- Lim LL, Hughes SJ, Hellawell EE. (2005). Integrated decision support system for urban air quality assessment. Environ Model Softw, 20: 947–954.
-
- Fang SH, Chen HW. (1996). Air quality and pollution control in Taiwan. Atmos Environ, 30: 735–741.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous