Clinical efficacy of novel elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) for diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules
- PMID: 30186965
- PMCID: PMC6119802
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.165
Clinical efficacy of novel elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) for diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules
Abstract
Objective: Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging is a recent ultrasound elastography technique; consequently, its efficacy is not fully known. In this study, we compared ARFI imaging with conventional strain elastography (SE) and shear wave velocities (SWVs) to evaluate the utility of ARFI imaging for diagnosing thyroid nodules.
Subjects and methods: In this study we examined 233 thyroid nodules (183 benign nodules and 50 malignant nodules) isolated from human patients. The nodules were evaluated with SE and ARFI imaging, and SWVs of the nodules were simultaneously measured. ARFI images were classified using a four-point score based on grayscale intensity of the images. The sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy were compared between SE and ARFI imaging. Finally, SWVs for each score of SE and ARFI imaging were compared.
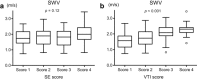
Results: The new scoring system for ARFI imaging can be divided into four virtual touch imaging (VTI) scores. Nodules with a VTI score of 3 or 4 as determined by ARFI imaging were determined to be malignant. The sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy, respectively, were 63.2%, 66.3%, and 65.6% for SE, compared with 80.0%, 86.3%, and 85.0% for ARFI imaging. The median SWVs of the nodules were 1.57 m/s, 1.73 m/s, 1.88 m/s, and 2.09 m/s for VTI scores of 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. The SWVs of VTI scores 3 and 4 were significantly higher than those of VTI scores 1 and 2.
Conclusions: The diagnostic accuracy of ARFI imaging for differentiating malignant thyroid nodules was higher than that of SE. The VTI scores of the nodules accurately reflected their SWVs.
Level of evidence: 4.
Keywords: ARFI; elastography; shear wave; thyroid nodule; ultrasonography.
Figures


References
-
- Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, et al. Thyroid gland tumor diagnosis at US elastography. Radiology 2005;237(1):202–211. - PubMed
-
- Park SH, Kim SJ, Kim EK, Kim MJ, Son EJ, Kwak JY. Interobserver agreement in assessing the sonographic and elastograpjic features of malignant thyroid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;193(5):W416–23. - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove D, Barr R, Bojunga J, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography: PART 4. Thyroid. Ultrasound Med Biol 2017;43(1):4–26. - PubMed
-
- Rago T, Santini F, Scutari M, Pinchera A, Vitti P. Elastography: new developments in ultrasound for predicting malignancy in thyroid nodules. J Clin Endo Metab 2007;92(8):2917–2922. - PubMed
-
- Tranquart F, Bleuzen A, Pierre‐Renoult P, Chabrolle C, Sam Giao M, Lecomte P. Elastosonography of thyroid lesions. J Radiol 2008;89(1):35–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
