The impact of extent of internal limiting membrane peeling on anatomical outcomes of macular hole surgery: results of a 54-week randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 30187641
- PMCID: PMC6585771
- DOI: 10.1111/aos.13853
The impact of extent of internal limiting membrane peeling on anatomical outcomes of macular hole surgery: results of a 54-week randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the anatomical outcomes of different extents of internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling in idiopathic macular hole surgery.
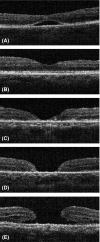
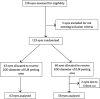
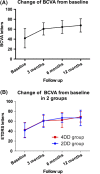
Methods: Prospective, parallel-group, randomized clinical trial. A total of 121 eyes of 121 patients with idiopathic macular hole underwent pars plana vitrectomy, and peeling of the ILM with a diameter of two disk diameters (DD) or 4DD based on randomization. The main outcome was the proportion of eyes with complete hole closure at 12 months. The second outcome was the hole closure grading stratified by macular hole closure index (MHCI) at each visit.
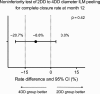
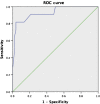
Results: At 12 months, there was no significant difference in anatomical outcomes with complete closure achieved in 52 (82.5%) of 63 eyes in the 2DD group and 53 (91.4%) of 58 eyes in the 4DD group (p = 0.15). For subjects with MHCI ≤0.5 (n = 24), complete closure rate was significantly lower in the 2DD group compared to the 4DD group (p = 0.012; 18.2% versus 75.9%, respectively). Average BCVA was lower in 2DD group than 4DD group (p = 0.014). By contrast, when MHCI was >0.5, the complete closure rate between the two groups showed no significant difference: 96.2% (50 patients) versus 95.6% (43 patients), respectively (p = 0.185).
Conclusion: In patients with idiopathic full-thickness macular hole and MHCI ≤0.5, a larger ILM peel of 4DD tends to achieve better anatomical outcomes than a more limited 2DD peel.
Keywords: anatomical outcomes; different diameter of internal limiting membrane peel; functional outcomes; internal limiting membrane peeling; macular hole.
© 2018 The Authors. Acta Ophthalmologica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelkader E & Lois N (2008): Internal limiting membrane peeling in vitreo‐retinal surgery. Surv Ophthalmol 53: 368–396. - PubMed
-
- Alkabes M, Salinas C, Vitale L, Burés‐Jelstrup A, Nucci P & Mateo C (2011): En face optical coherence tomography of inner retinal defects after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular hole. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52: 8349–8355. - PubMed
-
- Amouyal F, Shah SU, Pan CK, Schwartz SD & Hubschman JP (2014): Morphologic features and evolution of inner retinal dimples on optical coherence tomography after internal limiting membrane peeling. Retina 34: 2096–2102. - PubMed
-
- Bae K, Kang SW, Kim JH, Kim SJ, Kim JM & Yoon JM (2016): Extent of internal limiting membrane peeling and its impact on macular hole surgery outcomes: a randomized trial. Am J Ophthalmol 169: 179–188. - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge J, Herbert E & Gregor Z (2008): Macular holes: vitreoretinal relationships and surgical approaches. Eye 22: 1301–1309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

