The Curtius Rearrangement: Applications in Modern Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry
- PMID: 30187672
- PMCID: PMC6604631
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201800518
The Curtius Rearrangement: Applications in Modern Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry
Abstract
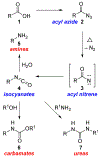
The Curtius rearrangement is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide derived from carboxylic acid to produce an isocyanate as the initial product. The isocyanate can undergo further reactions to provide amines and their derivatives. Due to its tolerance for a large variety of functional groups and complete retention of stereochemistry during rearrangement, the Curtius rearrangement has been used in the synthesis of a wide variety of medicinal agents with amines and amine-derived functional groups such as ureas and urethanes. The current review outlines various applications of the Curtius rearrangement in drug discovery and medicinal chemistry. In particular, the review highlights some widely used rearrangement methods, syntheses of some key agents for popular drug targets and FDA-approved drugs. In addition, the review highlights applications of the Curtius rearrangement in continuous-flow protocols for the scale-up of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Keywords: Curtius rearrangement; amine synthesis; carbamates; carboxylic acids; drug discovery; medicinal chemistry.
© 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



















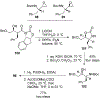
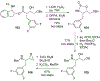

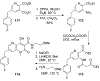
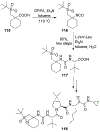


















Similar articles
-
The Curtius rearrangement: mechanistic insight and recent applications in natural product syntheses.Org Biomol Chem. 2018 Mar 28;16(12):2006-2027. doi: 10.1039/c8ob00138c. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Org Biomol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29479624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urea Derivatives in Modern Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry.J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 26;63(6):2751-2788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01541. Epub 2019 Dec 2. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31789518 Free PMC article.
-
Curtius rearrangement of aromatic carboxylic acids to access protected anilines and aromatic ureas.Org Lett. 2006 Dec 7;8(25):5717-20. doi: 10.1021/ol0622920. Org Lett. 2006. PMID: 17134255
-
TCT-mediated click chemistry for the synthesis of nitrogen-containing functionalities: conversion of carboxylic acids to carbamides, carbamates, carbamothioates, amides and amines.Org Biomol Chem. 2022 Jun 22;20(24):4942-4948. doi: 10.1039/d2ob00324d. Org Biomol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35660834
-
Recent applications of click chemistry in drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019 Aug;14(8):779-789. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2019.1614910. Epub 2019 May 16. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2019. PMID: 31094231 Review.
Cited by
-
Reaction of Picolinamides with Ketones Producing a New Type of Heterocyclic Salts with an Imidazolidin-4-One Ring.Molecules. 2023 Dec 29;29(1):206. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010206. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202789 Free PMC article.
-
A General N-alkylation Platform via Copper Metallaphotoredox and Silyl Radical Activation of Alkyl Halides.Chem. 2021 Jul 8;7(7):1827-1842. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2021.05.005. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Chem. 2021. PMID: 34423174 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Secondary Amines via Self-Limiting Alkylation.Org Lett. 2024 Jun 14;26(23):4926-4931. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.4c01430. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Org Lett. 2024. PMID: 38832812 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the synthesis of C-terminally modified peptides.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Sep 30;18(37):7253-7272. doi: 10.1039/d0ob01417f. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32914156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in urea- and thiourea-containing compounds: focus on innovative approaches in medicinal chemistry and organic synthesis.RSC Med Chem. 2021 May 13;12(7):1046-1064. doi: 10.1039/d1md00058f. eCollection 2021 Jul 21. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34355177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

