Beneficial Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats
- PMID: 30187703
- PMCID: PMC6127435
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.960
Beneficial Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats
Abstract
Purpose: Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) is an endogenous gaseous molecule with important physiological roles. It is synthesized from cysteine by cystathionine γ-lyase (CGL) and cystathionine β-synthase (CBS). The present study examined the benefits of exogenous H₂S on renal ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury, as well as the effects of CGL or CBS inhibition. Furthermore, we elucidated the mechanism underlying the action of H₂S in the kidneys.
Materials and methods: Thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to five groups: a sham, renal IR control, sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) treatment, H₂S donor, and CGL or CBS inhibitor administration group. Levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (Cr), renal tissue malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were estimated. Histological changes, apoptosis, and expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family members (extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38) were also evaluated.
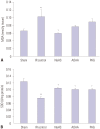
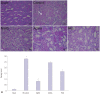
Results: NaHS attenuated serum BUN and Cr levels, as well as histological damage caused by renal IR injury. Administration of NaHS also reduced oxidative stress as evident from decreased MDA, preserved SOD, and reduced apoptotic cells. Additionally, NaHS prevented renal IR-induced MAPK phosphorylation. The CGL or CBS group showed increased MAPK family activity; however, there was no significant difference in the IR control group.
Conclusion: Exogenous H₂S can mitigate IR injury-led renal damage. The proposed beneficial effect of H₂S is, in part, because of the anti-oxidative stress associated with modulation of the MAPK signaling pathways.
Keywords: Hydrogen sulfide; cystathionine β-synthase; cystathionine γ-lyase; ischemia-reperfusion injury.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ischemia-reperfusion reduces cystathionine-beta-synthase-mediated hydrogen sulfide generation in the kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):F27-35. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00096.2009. Epub 2009 May 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19439522
-
Generation of endogenous hydrogen sulfide by cystathionine gamma-lyase limits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury and dysfunction.Lab Invest. 2008 Oct;88(10):1038-48. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2008.73. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Lab Invest. 2008. PMID: 18679378
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia abrogates fasting-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion by limiting bioavailability of hydrogen sulfide anions.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Aug;93(8):879-89. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1271-5. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25740079
-
Cystathionine beta-Synthase in hypoxia and ischemia/reperfusion: A current overview.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022 Mar 30;718:109149. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2022.109149. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35157853 Review.
-
The role of the mitochondrial trans-sulfuration in cerebro-cardio renal dysfunction during trisomy down syndrome.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Apr;479(4):825-829. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04761-9. Epub 2023 May 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37198322 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Update on Acute Kidney Injury-to-Chronic Kidney Disease Transition.Yonsei Med J. 2024 May;65(5):247-256. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0306. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 38653563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient electrochemiluminescence sensor utilizing Zr-PyTCPPMOF for swift hydrogen sulfide detection.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Dec 26;192(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06878-0. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39725807
-
NaHS protects brain, heart, and lungs as remote organs from renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in male and female rats.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Oct 22;25(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03824-3. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39438873 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous H2S Ameliorates High Salt-Induced Hypertension by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Paraventricular Nucleus in Dahl S Rats.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022 May;22(5):477-491. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09729-7. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35181841 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium hydrogen sulfide may not protect the kidney against ischemia/reperfusion damage in male and female rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2023 Mar 10;18(3):262-269. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.371582. eCollection 2023 May-Jun. Res Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37593161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Miller EJ, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Russell RR, 3rd, Young LH. AMP-activated protein kinase activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by increasing recruitment of p38 MAPK to TAB1 in the ischemic heart. Circ Res. 2005;97:872–879. - PubMed
-
- Yuan L, Wang J, Xiao H, Wu W, Wang Y, Liu X. MAPK signaling pathways regulate mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis induced by isoorientin in human hepatoblastoma cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;53:62–68. - PubMed
-
- Wang R. Two's company, three's a crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J. 2002;16:1792–1798. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

