High molecular weight hyaluronan ameliorates allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in the mouse
- PMID: 30188746
- PMCID: PMC6425518
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00009.2018
High molecular weight hyaluronan ameliorates allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in the mouse
Abstract
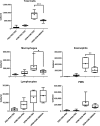
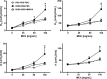
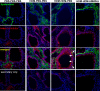
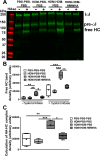
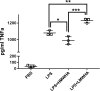
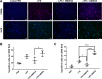
Allergic asthma is a major cause of morbidity in both pediatric and adult patients. Recent research has highlighted the role of hyaluronan (HA), an extracellular matrix glycosaminoglycan, in asthma pathogenesis. Experimental allergic airway inflammation and clinical asthma are associated with an increase of shorter fragments of HA (sHA), which complex with inter-α-inhibitor heavy chains (HCs) and induce inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR). Importantly, the effects of sHA can be antagonized by the physiological counterpart high molecular weight HA (HMWHA). We used a mouse model of house dust mite-induced allergic airway inflammation and demonstrated that instilled HMWHA ameliorated allergic airway inflammation and AHR, even when given after the establishment of allergic sensitization and after challenge exposures. Furthermore, instilled HMWHA reduced the development of HA-HC complexes and the activation of Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2. We conclude that airway application of HMWHA is a potential treatment for allergic airway inflammation.
Keywords: airway hyperresponsiveness; allergic asthma; hyaluronan; inflammation; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures




References
-
- Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Bailey C, Zahran HS, King M, Johnson CA, Liu X. Trends in asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality in the United States, 2001-2010. NCHS Data Brief 94: 1–8, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Liu X. Asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality: United States, 2005-2009. Natl Health Stat Report 32: 1–14, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Allegra L, Abraham WM, Fasano V, Petrigni G. Methacholine challenge in asthmatics is protected by aerosolised hyaluronan at high (1,000 kDa) but not low (300 kDa) molecular weight. G Ital Mal Torace 62: 297–301, 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

